Endogenous pro-resolving and anti-inflammatory lipid mediators: a new pharmacologic genus
- PMID: 17965751
- PMCID: PMC2268040
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707489
Endogenous pro-resolving and anti-inflammatory lipid mediators: a new pharmacologic genus
Abstract
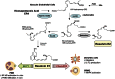
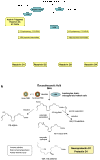
Complete resolution of an acute inflammatory response and its return to homeostasis are essential for healthy tissues. Here, we overview ongoing efforts to characterize cellular and molecular mechanisms that govern the resolution of self-limited inflammation. Systematic temporal analyses of evolving inflammatory exudates using mediator lipidomics-informatics, proteomics, and cellular trafficking with murine resolving exudates demonstrate novel endogenous pathways of local-acting mediators that share both anti-inflammatory and pro-resolving properties. In murine systems, resolving-exudate leukocytes switch their phenotype to actively generate new families of mediators from major omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA termed resolvins and protectins. Recent advances on their biosynthesis and actions are reviewed with a focus on the E-series resolvins (RvE1, RvE2), D series resolvins (RvD1, RvD2) and the protectins including neuroprotectin D1/protectin D1 (NPD1/PD1) as well as their aspirin-triggered epimeric forms. Members of each new family demonstrate potent stereo-specific actions, joining the lipoxins as endogenous local signals that govern resolution and endogenous anti-inflammation mechanisms. In addition to their origins and roles in resolution biology in the immune system, recent findings indicate that these new mediator families also display potent protective actions in lung, kidney, and eye as well as enhance microbial clearance. Thus, these endogenous agonists of resolution pathways constitute a novel genus of chemical mediators that possess pro-resolving, anti-inflammatory, and antifibrotic as well as host-directed antimicrobial actions. These may be useful in the design of new therapeutics and treatments for diseases with the underlying trait of uncontrolled inflammation and redox organ stress.
Figures

References
-
- Ariel A, Li P-L, Wang W, Tang W-X, Fredman G, Hong S, et al. The docosatriene protectin D1 is produced by TH2 skewing and promotes human T cell apoptosis via lipid raft clustering. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:43079–43086. - PubMed
-
- Arita M, Clish CB, Serhan CN. The contributions of aspirin and microbial oxygenase in the biosynthesis of anti-inflammatory resolvins: novel oxygenase products from omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. Biochem Biophy Res Commun. 2005b;338:149–157. - PubMed
-
- Arita M, Oh S, Chonan T, Hong S, Elangovan S, Sun Y-P, et al. Metabolic inactivation of resolvin E1 and stabilization of its anti-inflammatory actions. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:22847–22854. - PubMed
-
- Arita M, Ohira T, Sun YP, Elangovan S, Chiang N, Serhan CN. Resolvin E1 selectively interacts with leukotriene B4 receptor BLT1 and ChemR23 to regulate inflammation. J Immunol. 2007;178:3912–3917. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

