'Unite and conquer': enhanced prediction of protein subcellular localization by integrating multiple specialized tools
- PMID: 17967180
- PMCID: PMC2176073
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-8-420
'Unite and conquer': enhanced prediction of protein subcellular localization by integrating multiple specialized tools
Abstract
Background: Knowing the subcellular location of proteins provides clues to their function as well as the interconnectivity of biological processes. Dozens of tools are available for predicting protein location in the eukaryotic cell. Each tool performs well on certain data sets, but their predictions often disagree for a given protein. Since the individual tools each have particular strengths, we set out to integrate them in a way that optimally exploits their potential. The method we present here is applicable to various subcellular locations, but tailored for predicting whether or not a protein is localized in mitochondria. Knowledge of the mitochondrial proteome is relevant to understanding the role of this organelle in global cellular processes.
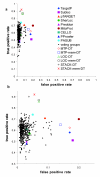
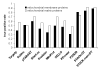
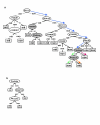
Results: In order to develop a method for enhanced prediction of subcellular localization, we integrated the outputs of available localization prediction tools by several strategies, and tested the performance of each strategy with known mitochondrial proteins. The accuracy obtained (up to 92%) surpasses by far the individual tools. The method of integration proved crucial to the performance. For the prediction of mitochondrion-located proteins, integration via a two-layer decision tree clearly outperforms simpler methods, as it allows emphasis of biologically relevant features such as the mitochondrial targeting peptide and transmembrane domains.
Conclusion: We developed an approach that enhances the prediction accuracy of mitochondrial proteins by uniting the strength of specialized tools. The combination of machine-learning based integration with biological expert knowledge leads to improved performance. This approach also alleviates the conundrum of how to choose between conflicting predictions. Our approach is easy to implement, and applicable to predicting subcellular locations other than mitochondria, as well as other biological features. For a trial of our approach, we provide a webservice for mitochondrial protein prediction (named YimLOC), which can be accessed through the AnaBench suite at http://anabench.bcm.umontreal.ca/anabench/. The source code is provided in the Additional File 2.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TESTLoc: protein subcellular localization prediction from EST data.BMC Bioinformatics. 2010 Nov 15;11:563. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-563. BMC Bioinformatics. 2010. PMID: 21078192 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of protein subcellular localization.Proteins. 2006 Aug 15;64(3):643-51. doi: 10.1002/prot.21018. Proteins. 2006. PMID: 16752418
-
An SVM-based system for predicting protein subnuclear localizations.BMC Bioinformatics. 2005 Dec 7;6:291. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-6-291. BMC Bioinformatics. 2005. PMID: 16336650 Free PMC article.
-
State-of-the-art bioinformatics protein structure prediction tools (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2011 Sep;28(3):295-310. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2011.705. Epub 2011 May 23. Int J Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 21617841 Review.
-
Protein Sorting Prediction.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1615:23-57. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7033-9_2. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28667600 Review.
Cited by
-
Diversity and dispersal of a ubiquitous protein family: acyl-CoA dehydrogenases.Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Sep;37(17):5619-31. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp566. Epub 2009 Jul 22. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 19625492 Free PMC article.
-
The use of classification trees for bioinformatics.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Data Min Knowl Discov. 2011 Jan;1(1):55-63. doi: 10.1002/widm.14. Epub 2011 Jan 6. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Data Min Knowl Discov. 2011. PMID: 22523608 Free PMC article.
-
Minimalist ensemble algorithms for genome-wide protein localization prediction.BMC Bioinformatics. 2012 Jul 3;13:157. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-13-157. BMC Bioinformatics. 2012. PMID: 22759391 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding molecular mechanisms of disease through spatial proteomics.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2019 Feb;48:19-25. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2018.09.016. Epub 2018 Oct 9. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2019. PMID: 30308467 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TESTLoc: protein subcellular localization prediction from EST data.BMC Bioinformatics. 2010 Nov 15;11:563. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-563. BMC Bioinformatics. 2010. PMID: 21078192 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chou KC, Shen HB. Euk-mPLoc: a fusion classifier for large-scale eukaryotic protein subcellular location prediction by incorporating multiple sites. J Proteome Res. 2007;6:1728–1734. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

