NF-kappa B-mediated adaptive resistance to ionizing radiation
- PMID: 17967430
- PMCID: PMC2266095
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2007.09.022
NF-kappa B-mediated adaptive resistance to ionizing radiation
Abstract
Ionizing radiation (IR) began to be a powerful medical modality soon after Wilhelm Röntgen's discovery of X-rays in 1895. Today, more than 50% of cancer patients receive radiotherapy at some time during the course of their disease. Recent technical developments have significantly increased the precision of dose delivery to the target tumor, making radiotherapy more efficient in cancer treatment. However, tumor cells have been shown to acquire a radioresistance that has been linked to increased recurrence and failure in many patients. The exact mechanisms by which tumor cells develop an adaptive resistance to therapeutic fractional irradiation are unknown, although low-dose IR has been well defined for radioadaptive protection of normal cells. This review will address the radioadaptive response, emphasizing recent studies of molecular-level reactions. A prosurvival signaling network initiated by the transcription factor NF-kappa B, DNA-damage sensor ATM, oncoprotein HER-2, cell cyclin elements (cyclin B1), and mitochondrial functions in radioadaptive resistance is discussed. Further elucidation of the key elements in this prosurvival network may generate novel targets for resensitizing the radioresistant tumor cells.
Figures

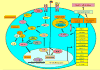
References
-
- Kim JJ, Tannock IF. Repopulation of cancer cells during therapy: an important cause of treatment failure. Nat Rev, Cancer. 2005;5:516–525. - PubMed
-
- Stecca C, Gerber GB. Adaptive response to DNA-damaging agents: a review of potential mechanisms. Biochem Pharmacol. 1998;55:941–951. - PubMed
-
- Olivieri G, Bodycote J, Wolff S. Adaptive response of human lymphocytes to low concentrations of radioactive thymidine. Science. 1994;223:594–597. - PubMed
-
- Kelsey KT, Memisoglu A, Frenkel D, Liber HL. Human lymphocytes exposed to low doses of X-rays are less susceptible to radiation-induced mutagenesis. Mutat Res. 1991;263:197–201. - PubMed
-
- Feinendegen LE, Bond VP, Sondhaus CA, Muehlensiepen H. Radiation effects induced by low doses in complex tissue and their relation to cellular adaptive responses. Mutat Res. 1996;358:199–205. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

