Auditory brainstem responses are impaired in EphA4 and ephrin-B2 deficient mice
- PMID: 17967521
- PMCID: PMC3250224
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heares.2007.09.003
Auditory brainstem responses are impaired in EphA4 and ephrin-B2 deficient mice
Abstract
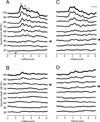
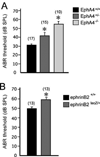
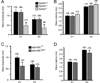
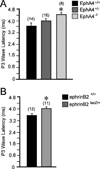
The Eph receptor tyrosine kinases and their membrane-anchored ligands, ephrins, are signaling proteins that act as axon guidance molecules during chick auditory brainstem development. We recently showed that Eph proteins also affect patterns of neural activation in the mammalian brainstem. However, functional deficits in the brainstems of mutant mice have not been assessed physiologically. The present study characterizes neural activation in Eph protein deficient mice in the auditory brainstem response (ABR). We recorded the ABR of EphA4 and ephrin-B2 mutant mice, aged postnatal day 18-20, and compared them to wild type controls. The peripheral hearing threshold of EphA4(-/-) mice was 75% higher than that of controls. Waveform amplitudes of peak 1 (P1) were 54% lower in EphA4(-/-) mice than in controls. The peripheral hearing thresholds in ephrin-B2(lacZ/)(+) mice were also elevated, with a mean value 20% higher than that of controls. These ephrin-B2(lacZ/)(+) mice showed a 38% smaller P1 amplitude. Significant differences in latency to waveform peaks were also observed. These elevated thresholds and reduced peak amplitudes provide evidence for hearing deficits in both of these mutant mouse lines, and further emphasize an important role for Eph family proteins in the formation of functional auditory circuitry.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Auditory brainstem neural activation patterns are altered in EphA4- and ephrin-B2-deficient mice.J Comp Neurol. 2007 Dec 20;505(6):669-81. doi: 10.1002/cne.21530. J Comp Neurol. 2007. PMID: 17948875
-
Graded and discontinuous EphA-ephrinB expression patterns in the developing auditory brainstem.Hear Res. 2016 May;335:64-75. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2016.02.013. Epub 2016 Feb 21. Hear Res. 2016. PMID: 26906676 Free PMC article.
-
EphA4 and ephrin-B2 expression patterns during inferior colliculus projection shaping prior to experience.Dev Neurobiol. 2011 Feb;71(2):182-99. doi: 10.1002/dneu.20842. Dev Neurobiol. 2011. PMID: 20886601
-
Roles of Eph receptors and ephrins in segmental patterning.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2000 Jul 29;355(1399):993-1002. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2000.0635. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2000. PMID: 11128993 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Eph and ephrin signaling in the development of the central auditory system.Dev Dyn. 2023 Jan;252(1):10-26. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.506. Epub 2022 Jun 24. Dev Dyn. 2023. PMID: 35705527 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Building thalamic neuronal networks during mouse development.Front Neural Circuits. 2023 Feb 3;17:1098913. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2023.1098913. eCollection 2023. Front Neural Circuits. 2023. PMID: 36817644 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EphrinB1 expression is dysregulated and promotes oncogenic signaling in medulloblastoma.J Neurooncol. 2015 Jan;121(1):109-18. doi: 10.1007/s11060-014-1618-8. Epub 2014 Sep 26. J Neurooncol. 2015. PMID: 25258252 Free PMC article.
-
EphB signaling regulates target innervation in the developing and deafferented auditory brainstem.Dev Neurobiol. 2012 Sep;72(9):1243-55. doi: 10.1002/dneu.20990. Epub 2012 Jun 21. Dev Neurobiol. 2012. PMID: 22021100 Free PMC article.
-
Ephrin-A5/EphA4 signalling controls specific afferent targeting to cochlear hair cells.Nat Commun. 2013;4:1438. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2445. Nat Commun. 2013. PMID: 23385583
-
Ephrin-B reverse signaling is required for formation of strictly contralateral auditory brainstem pathways.J Neurosci. 2010 Jul 21;30(29):9840-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0386-10.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20660266 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

