Transcriptional adaptor ADA3 of Drosophila melanogaster is required for histone modification, position effect variegation, and transcription
- PMID: 17967867
- PMCID: PMC2223303
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01307-07
Transcriptional adaptor ADA3 of Drosophila melanogaster is required for histone modification, position effect variegation, and transcription
Abstract
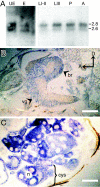
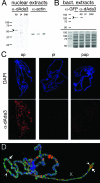
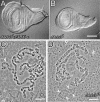
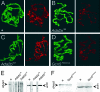
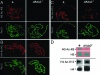
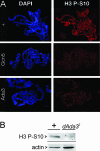
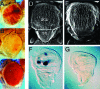
The Drosophila melanogaster gene diskette (also known as dik or dAda3) encodes a protein 29% identical to human ADA3, a subunit of GCN5-containing histone acetyltransferase (HAT) complexes. The fly dADA3 is a major contributor to oogenesis, and it is also required for somatic cell viability. dADA3 localizes to chromosomes, and it is significantly reduced in dGcn5 and dAda2a, but not in dAda2b, mutant backgrounds. In dAda3 mutants, acetylation at histone H3 K9 and K14, but not K18, and at histone H4 K12, but not K5, K8, and K16, is significantly reduced. Also, phosphorylation at H3 S10 is reduced in dAda3 and dGcn5 mutants. Variegation for white (w(m4)) and scute (Hw(v)) genes, caused by rearrangements of X chromosome heterochromatin, is modified in a dAda3(+) gene-dosage-dependent manner. The effect is not observed with rearrangements involving Y heterochromatin (bw(D)), euchromatin (Scutoid), or transvection effects on chromosomal pairing (white and zeste interaction). Activity of scute gene enhancers, targets for Iroquoi transcription factors, is abolished in dAda3 mutants. Also, Iroquoi-associated phenotypes are sensitive to dAda3(+) gene dosage. We conclude that dADA3 plays a role in HAT complexes which acetylate H3 and H4 at specific residues. In turn, this acetylation results in chromatin structure effects of certain rearrangements and transcription of specific genes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
GAL4 induces transcriptionally active puff in the absence of dSAGA- and ATAC-specific chromatin acetylation in the Drosophila melanogaster polytene chromosome.Chromosoma. 2009 Aug;118(4):513-26. doi: 10.1007/s00412-009-0215-7. Epub 2009 May 2. Chromosoma. 2009. PMID: 19412618
-
The Drosophila histone acetyltransferase Gcn5 and transcriptional adaptor Ada2a are involved in nucleosomal histone H4 acetylation.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Dec;26(24):9413-23. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01401-06. Epub 2006 Oct 9. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 17030603 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila Ada2b is required for viability and normal histone H3 acetylation.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Sep;24(18):8080-9. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.18.8080-8089.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15340070 Free PMC article.
-
The Gcn5 complexes in Drosophila as a model for metazoa.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2021 Feb;1864(2):194610. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2020.194610. Epub 2020 Jul 28. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2021. PMID: 32735945 Review.
-
The Ada2/Ada3/Gcn5/Sgf29 histone acetyltransferase module.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2021 Feb;1864(2):194629. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2020.194629. Epub 2020 Sep 2. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2021. PMID: 32890768 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genes of the ecdysone biosynthesis pathway are regulated by the dATAC histone acetyltransferase complex in Drosophila.Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Sep;30(17):4254-66. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00142-10. Epub 2010 Jun 28. Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20584983 Free PMC article.
-
Modularity of CHIP/LDB transcription complexes regulates cell differentiation.Fly (Austin). 2011 Jul-Sep;5(3):200-5. doi: 10.4161/fly.5.3.14854. Epub 2011 Jul 1. Fly (Austin). 2011. PMID: 21406967 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct contributions of MSL complex subunits to the transcriptional enhancement responsible for dosage compensation in Drosophila.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Dec;40(22):11281-91. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks890. Epub 2012 Oct 9. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 23047951 Free PMC article.
-
GAL4 induces transcriptionally active puff in the absence of dSAGA- and ATAC-specific chromatin acetylation in the Drosophila melanogaster polytene chromosome.Chromosoma. 2009 Aug;118(4):513-26. doi: 10.1007/s00412-009-0215-7. Epub 2009 May 2. Chromosoma. 2009. PMID: 19412618
-
Conservation and diversity of the eukaryotic SAGA coactivator complex across kingdoms.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2021 Jun 10;14(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s13072-021-00402-x. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2021. PMID: 34112237 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Balasubramanian, R., M. G. Pray-Grant, W. Selleck, P. A. Grant, and S. Tan. 2002. Role of the Ada2 and Ada3 transcriptional coactivators in histone acetylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2777989-7995. - PubMed
-
- Baumann, A., I. Krah-Jentgens, R. Muller, F. Muller-Holtkamp, R. Seidel, N. Kecskemethy, J. Casal, A. Ferrus, and O. Pongs. 1987. Molecular organization of the maternal effect region of the Shaker complex of Drosophila: characterization of an I(A) channel transcript with homology to vertebrate Na channel. EMBO J. 63419-3429. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berger, S. L. 1999. Gene activation by histone and factor acetyltransferases. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 11336-341. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
