A-raf and B-raf are dispensable for normal endochondral bone development, and parathyroid hormone-related peptide suppresses extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation in hypertrophic chondrocytes
- PMID: 17967876
- PMCID: PMC2223319
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00617-07
A-raf and B-raf are dispensable for normal endochondral bone development, and parathyroid hormone-related peptide suppresses extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation in hypertrophic chondrocytes
Abstract
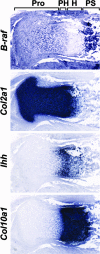
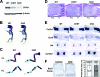
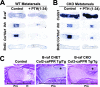
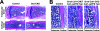
Parathyroid hormone-related peptide (PTHrP) and the parathyroid hormone-PTHrP receptor increase chondrocyte proliferation and delay chondrocyte maturation in endochondral bone development at least partly through cyclic AMP (cAMP)-dependent signaling pathways. Because data suggest that the ability of cAMP to stimulate cell proliferation involves the mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase B-Raf, we hypothesized that B-Raf might mediate the proliferative action of PTHrP in chondrocytes. Though B-Raf is expressed in proliferative chondrocytes, its conditional removal from cartilage did not affect chondrocyte proliferation and maturation or PTHrP-induced chondrocyte proliferation and PTHrP-delayed maturation. Similar results were obtained by conditionally removing B-Raf from osteoblasts. Because A-raf and B-raf are expressed similarly in cartilage, we speculated that they may fulfill redundant functions in this tissue. Surprisingly, mice with chondrocytes deficient in both A-Raf and B-Raf exhibited normal endochondral bone development. Activated extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) was detected primarily in hypertrophic chondrocytes, where C-raf is expressed, and the suppression of ERK activation in these cells by PTHrP or a MEK inhibitor coincided with a delay in chondrocyte maturation. Taken together, these results demonstrate that B-Raf and A-Raf are dispensable for endochondral bone development and they indicate that the main role of ERK in cartilage is to stimulate not cell proliferation, but rather chondrocyte maturation.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Raf Kinases Are Essential for Phosphate Induction of ERK1/2 Phosphorylation in Hypertrophic Chondrocytes and Normal Endochondral Bone Development.J Biol Chem. 2017 Feb 24;292(8):3164-3171. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.763342. Epub 2017 Jan 10. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28073913 Free PMC article.
-
PTHrP targets HDAC4 and HDAC5 to repress chondrocyte hypertrophy.JCI Insight. 2019 Mar 7;4(5):e97903. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.97903. eCollection 2019 Mar 7. JCI Insight. 2019. PMID: 30843886 Free PMC article.
-
ALK2 functions as a BMP type I receptor and induces Indian hedgehog in chondrocytes during skeletal development.J Bone Miner Res. 2003 Sep;18(9):1593-604. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.2003.18.9.1593. J Bone Miner Res. 2003. PMID: 12968668
-
Parathyroid hormone-related protein (PTHrP) as a regulating factor of endochondral bone formation.Oral Dis. 1997 Dec;3(4):229-31. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-0825.1997.tb00046.x. Oral Dis. 1997. PMID: 9643217 Review.
-
Interaction of growth factors regulating chondrocyte differentiation in the developing embryo.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2001;9 Suppl A:S109-17. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2001. PMID: 11680674 Review.
Cited by
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 (ERK1) and ERK2 play essential roles in osteoblast differentiation and in supporting osteoclastogenesis.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Nov;29(21):5843-57. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01549-08. Epub 2009 Sep 8. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19737917 Free PMC article.
-
c-Raf promotes angiogenesis during normal growth plate maturation.Development. 2016 Jan 15;143(2):348-55. doi: 10.1242/dev.127142. Epub 2015 Dec 10. Development. 2016. PMID: 26657770 Free PMC article.
-
Phlpp1 alters the murine chondrocyte phospho-proteome during endochondral bone formation.Bone. 2024 Dec;189:117265. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2024.117265. Epub 2024 Sep 29. Bone. 2024. PMID: 39349089
-
Raf Kinases Are Essential for Phosphate Induction of ERK1/2 Phosphorylation in Hypertrophic Chondrocytes and Normal Endochondral Bone Development.J Biol Chem. 2017 Feb 24;292(8):3164-3171. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.763342. Epub 2017 Jan 10. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28073913 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies to minimize hypertrophy in cartilage engineering and regeneration.Genes Dis. 2015 Mar 1;2(1):76-95. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2014.12.003. Genes Dis. 2015. PMID: 26000333 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Calvi, L. M., N. A. Sims, J. L. Hunzelman, M. C. Knight, A. Giovannetti, J. M. Saxton, H. M. Kronenberg, R. Baron, and E. Schipani. 2001. Activated parathyroid hormone/parathyroid hormone-related protein receptor in osteoblastic cells differentially affects cortical and trabecular bone. J. Clin. Investig. 107277-286. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen, A. P., M. Ohno, K. P. Giese, R. Kuhn, R. L. Chen, and A. J. Silva. 2006. Forebrain-specific knockout of B-raf kinase leads to deficits in hippocampal long-term potentiation, learning, and memory. J. Neurosci. Res. 8328-38. - PubMed
-
- Chen, C., A. J. Koh, N. S. Datta, J. Zhang, E. T. Keller, G. Xiao, R. T. Franceschi, N. J. D'Silva, and L. K. McCauley. 2004. Impact of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway on parathyroid hormone-related protein actions in osteoblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 27929121-29129. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
