Cancer-causing mutations in a novel transcription-dependent nuclear export motif of VHL abrogate oxygen-dependent degradation of hypoxia-inducible factor
- PMID: 17967880
- PMCID: PMC2223288
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01044-07
Cancer-causing mutations in a novel transcription-dependent nuclear export motif of VHL abrogate oxygen-dependent degradation of hypoxia-inducible factor
Abstract
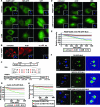
It is thought that degradation of nuclear proteins by the ubiquitylation system requires nuclear-cytoplasmic trafficking of E3 ubiquitin ligases. The von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) tumor suppressor protein is the substrate recognition component of a Cullin-2-containing E3 ubiquitin ligase that recruits hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) for oxygen-dependent degradation. We demonstrated that VHL engages in nuclear-cytoplasmic trafficking that requires ongoing transcription to promote efficient HIF degradation. Here, we report the identification of a discreet motif, DXGX(2)DX(2)L, that directs transcription-dependent nuclear export of VHL and which is targeted by naturally occurring mutations associated with renal carcinoma and polycythemia in humans. The DXGX(2)DX(2)L motif is also found in other proteins, including poly(A)-binding protein 1, to direct its transcription-dependent nuclear export. We define DXGX(2)DX(2)L as TD-NEM (transcription-dependent nuclear export motif), since inhibition of transcription by actinomycin D or 5,6-dichlorobenzimidazole abrogates its nuclear export activity. Disease-causing mutations of key residues of TD-NEM restrain the ability of VHL to efficiently mediate oxygen-dependent degradation of HIF by altering its nuclear export dynamics without affecting interaction with its substrate. These results identify a novel nuclear export motif, further highlight the role of nuclear-cytoplasmic shuttling of E3 ligases in degradation of nuclear substrates, and provide evidence that disease-causing mutations can target subcellular trafficking.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Subcellular dynamics of the VHL tumor suppressor: on the move for HIF degradation.Future Oncol. 2009 Feb;5(1):85-95. doi: 10.2217/14796694.5.1.85. Future Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19243301 Review.
-
Oxygen-dependent ubiquitination and degradation of hypoxia-inducible factor requires nuclear-cytoplasmic trafficking of the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Aug;22(15):5319-36. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.15.5319-5336.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12101228 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription-dependent nuclear-cytoplasmic trafficking is required for the function of the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein.Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Feb;19(2):1486-97. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.2.1486. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 9891082 Free PMC article.
-
Role of exon 2-encoded beta -domain of the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein.J Biol Chem. 2001 Jan 12;276(2):1407-16. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M008295200. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11024059
-
The VHL tumor suppressor and HIF: insights from genetic studies in mice.Cell Death Differ. 2008 Apr;15(4):650-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4402313. Epub 2008 Jan 25. Cell Death Differ. 2008. PMID: 18219317 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
eEF1A is a novel component of the mammalian nuclear protein export machinery.Mol Biol Cell. 2008 Dec;19(12):5296-308. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e08-06-0562. Epub 2008 Sep 17. Mol Biol Cell. 2008. PMID: 18799616 Free PMC article.
-
Proteome-wide search for functional motifs altered in tumors: Prediction of nuclear export signals inactivated by cancer-related mutations.Sci Rep. 2016 May 12;6:25869. doi: 10.1038/srep25869. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27174732 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Ran-regulated nuclear-cytoplasmic trafficking of pVHL in the regulation of microtubular stability-mediated HIF-1α in hypoxic cardiomyocytes.Sci Rep. 2015 Mar 17;5:9193. doi: 10.1038/srep09193. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25779090 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear-cytoplasmatic shuttling of proteins in control of cellular oxygen sensing.J Mol Med (Berl). 2015 Jun;93(6):599-608. doi: 10.1007/s00109-015-1276-0. Epub 2015 Mar 27. J Mol Med (Berl). 2015. PMID: 25809665 Review.
References
-
- Afonina, E., R. Stauber, and G. N. Pavlakis. 1998. The human poly(A)-binding protein 1 shuttles between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. J. Biol. Chem. 27313015-13021. - PubMed
-
- Bonicalzi, M. E., I. Groulx, N. de Paulsen, and S. Lee. 2001. Role of exon 2-encoded beta-domain of the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2761407-1416. - PubMed
-
- Bruick, R. K., and S. L. McKnight. 2001. A conserved family of prolyl-4-hydroxylases that modify HIF. Science 2941337-1340. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
