Certain and progressive methylation of histone H4 at lysine 20 during the cell cycle
- PMID: 17967882
- PMCID: PMC2223297
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01517-07
Certain and progressive methylation of histone H4 at lysine 20 during the cell cycle
Abstract
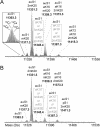
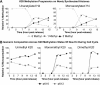
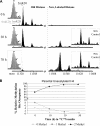
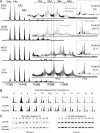
Methylation of histone H4 at lysine 20 (K20) has been implicated in transcriptional activation, gene silencing, heterochromatin formation, mitosis, and DNA repair. However, little is known about how this modification is regulated or how it contributes to these diverse processes. Metabolic labeling and top-down mass spectrometry reveal that newly synthesized H4 is progressively methylated at K20 during the G(2), M, and G(1) phases of the cell cycle in a process that is largely inescapable and irreversible. Approximately 98% of new H4 becomes dimethylated within two to three cell cycles, and K20 methylation turnover in vivo is undetectable. New H4 is methylated regardless of prior acetylation, and acetylation occurs predominantly on K20-dimethylated H4, refuting the hypothesis that K20 methylation antagonizes H4 acetylation and represses transcription epigenetically. Despite suggestions that it is required for normal mitosis and cell cycle progression, K20 methylation proceeds normally during colchicine treatment. Moreover, delays in PR-Set7 synthesis and K20 methylation which accompany altered cell cycle progression during sodium butyrate treatment appear to be secondary to histone hyperacetylation or other effects of butyrate since depletion of PR-Set7 did not affect cell cycle progression. Together, our data provide an unbiased perspective of the regulation and function of K20 methylation.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Purification and functional characterization of SET8, a nucleosomal histone H4-lysine 20-specific methyltransferase.Curr Biol. 2002 Jul 9;12(13):1086-99. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(02)00924-7. Curr Biol. 2002. PMID: 12121615
-
Mitotic-specific methylation of histone H4 Lys 20 follows increased PR-Set7 expression and its localization to mitotic chromosomes.Genes Dev. 2002 Sep 1;16(17):2225-30. doi: 10.1101/gad.1014902. Genes Dev. 2002. PMID: 12208845 Free PMC article.
-
A switch in mitotic histone H4 lysine 20 methylation status is linked to M phase defects upon loss of HCF-1.Mol Cell. 2004 Jun 18;14(6):713-25. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2004.06.008. Mol Cell. 2004. PMID: 15200950
-
The multiple facets of histone H4-lysine 20 methylation.Biochem Cell Biol. 2009 Feb;87(1):151-61. doi: 10.1139/O08-131. Biochem Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19234531 Review.
-
[The roles of histone lysine methylation in epigenetic regulation].Yi Chuan. 2007 Apr;29(4):387-92. doi: 10.1360/yc-007-0387. Yi Chuan. 2007. PMID: 17548299 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Deacetylation of H4-K16Ac and heterochromatin assembly in senescence.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2012 Aug 29;5(1):15. doi: 10.1186/1756-8935-5-15. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2012. PMID: 22932127 Free PMC article.
-
The patterns and participants of parental histone recycling during DNA replication in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Sci China Life Sci. 2023 Jul;66(7):1600-1614. doi: 10.1007/s11427-022-2267-6. Epub 2023 Mar 9. Sci China Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 36914923
-
Epigenetic landscape for initiation of DNA replication.Chromosoma. 2014 Jun;123(3):183-99. doi: 10.1007/s00412-013-0448-3. Epub 2013 Dec 17. Chromosoma. 2014. PMID: 24337246 Review.
-
Monomethylation of histone H4-lysine 20 is involved in chromosome structure and stability and is essential for mouse development.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Apr;29(8):2278-95. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01768-08. Epub 2009 Feb 17. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19223465 Free PMC article.
-
Functional analysis of boundary regions of forum domains.Dokl Biochem Biophys. 2008 Nov-Dec;423:342-5. doi: 10.1134/s1607672908060069. Dokl Biochem Biophys. 2008. PMID: 19230384 No abstract available.
References
-
- Barber, C. M., F. B. Turner, Y. Wang, K. Hagstrom, S. D. Taverna, S. Mollah, B. Ueberheide, B. J. Meyer, D. F. Hunt, P. Cheung, and C. D. Allis. 2004. The enhancement of histone H4 and H2A serine 1 phosphorylation during mitosis and S-phase is evolutionarily conserved. Chromosoma 112360-371. - PubMed
-
- Barski, A., S. Cuddapah, K. Cui, T. Y. Roh, D. E. Schones, Z. Wang, G. Wei, I. Chepelev, and K. Zhao. 2007. High-resolution profiling of histone methylations in the human genome. Cell 129823-837. - PubMed
-
- Beisel, C., A. Imhof, J. Greene, E. Kremmer, and F. Sauer. 2002. Histone methylation by the Drosophila epigenetic transcriptional regulator Ash1. Nature 419857-862. - PubMed
-
- Boyne, M. T., II, J. J. Pesavento, C. A. Mizzen, and N. L. Kelleher. 2006. Precise characterization of human histones in the H2A gene family by top down mass spectrometry. J. Proteome Res. 5248-253. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
