Comparative evaluation of the inhibitory activities of a series of pyrimidinedione congeners that inhibit human immunodeficiency virus types 1 and 2
- PMID: 17967909
- PMCID: PMC2223882
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00972-07
Comparative evaluation of the inhibitory activities of a series of pyrimidinedione congeners that inhibit human immunodeficiency virus types 1 and 2
Abstract
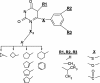
Seventy-three analogs of SJ-3366 (1-(3-cyclopenten-1-ylmethyl)-5-ethyl-6-(3,5-dimethylbenzoyl)-2,4(1H,3H)-pyrimidinedione) were synthesized and comparatively evaluated for their ability to inhibit the replication of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) and HIV-2 and for their ability to suppress virus entry and reverse transcription. These studies were performed to identify inhibitors with activity greater than that of the current lead molecule (SJ-3366) and to utilize structure-activity relationships (SAR) to define the chemical features of the pyrimidinedione congeners responsible for their efficacy, toxicity, and dual mechanism of action against HIV. The results of our SAR evaluations have demonstrated that the addition of the homocyclic moiety at the N-1 of the pyrimidinedione results in acquisition of the ability to inhibit virus entry and extends the range of action of the compounds to include HIV-2. In addition, the results demonstrate that analogs with a methyl linker between the homocyclic substitution and the N-1 of the pyrimidinedione had a greater number of highly active molecules than those analogs possessing ethyl linkers. Six molecules were identified with activity equivalent to or greater than that of SJ-3366, and five additional molecules with highly potent inhibition of reverse transcriptase and virus entry and possessing high efficacy against both HIV-1 and HIV-2 were identified. Six molecules exhibited significant inhibition of viruses with the highly problematic nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI) resistance engendering amino acid change K103N in the reverse transcriptase. These evaluations indicate that a new class of NNRTIs has been identified and that these NNRTIs possess highly potent inhibition of HIV-1 with an extended range of action, which now includes HIV-2.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SJ-3366, a unique and highly potent nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) that also inhibits HIV-2.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001 Feb;45(2):393-400. doi: 10.1128/AAC.45.2.393-400.2001. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001. PMID: 11158731 Free PMC article.
-
The structure-activity relationships of 2,4(1H,3H)-pyrimidinedione derivatives as potent HIV type 1 and type 2 inhibitors.Antivir Chem Chemother. 2007;18(5):259-75. doi: 10.1177/095632020701800502. Antivir Chem Chemother. 2007. PMID: 18046959
-
Unique anti-human immunodeficiency virus activities of the nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors calanolide A, costatolide, and dihydrocostatolide.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1999 Aug;43(8):1827-34. doi: 10.1128/AAC.43.8.1827. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1999. PMID: 10428899 Free PMC article.
-
Efavirenz a nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor of first-generation: Approaches based on its medicinal chemistry.Eur J Med Chem. 2016 Jan 27;108:455-465. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2015.11.025. Epub 2015 Nov 25. Eur J Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 26708112 Review.
-
Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel acetamide-substituted doravirine and its prodrugs as potent HIV-1 NNRTIs.Bioorg Med Chem. 2019 Feb 1;27(3):447-456. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2018.12.039. Epub 2018 Dec 30. Bioorg Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30606670 Review.
Cited by
-
Preclinical evaluation of a mercaptobenzamide and its prodrug for NCp7-targeted inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus.Antiviral Res. 2016 Oct;134:216-225. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2016.08.022. Epub 2016 Aug 26. Antiviral Res. 2016. PMID: 27568924 Free PMC article.
-
Antiviral interactions of combinations of highly potent 2,4(1H,3H)-pyrimidinedione congeners and other anti-HIV agents.Antiviral Res. 2011 Dec;92(3):505-8. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2011.10.013. Epub 2011 Oct 19. Antiviral Res. 2011. PMID: 22036651 Free PMC article.
-
Topical prophylaxis for HIV prevention in women: becoming a reality.Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2011 Jun;8(2):104-13. doi: 10.1007/s11904-011-0075-7. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2011. PMID: 21424725 Free PMC article.
-
Safe and sustained vaginal delivery of pyrimidinedione HIV-1 inhibitors from polyurethane intravaginal rings.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 Mar;56(3):1291-9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.05721-11. Epub 2011 Dec 12. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012. PMID: 22155820 Free PMC article.
-
Double Variational Binding--(SMILES) Conformational Analysis by Docking Mechanisms for Anti-HIV Pyrimidine Ligands.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Aug 18;16(8):19553-601. doi: 10.3390/ijms160819553. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26295229 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baba, M., S. Shigeta, H. Tanaka, T. Miyasaka, M. Ubasawa, K. Umezu, R. T. Walker, R. Pauwels, and E. De Clercq. 1992. Highly potent and selective inhibition of HIV-1 replication by 6-phenylthiouracil derivatives. Antivir. Res. 17:245-264. - PubMed
-
- Baba, M., S. Shigeta, S. Yuasa, H. Takashima, K. Sekiya, M. Ubasawa, H. Tanaka, T. Miyasaka, R. T. Walker, and E. De Clercq. 1994. Preclinical evaluation of MKC-442, a highly potent and specific inhibitor of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in vitro. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 38:688-692. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baba, M., H. Tanaka, E. De Clercq, R. Pauwels, J. Balzarini, D. Schols, H. Nakashima, C. F. Perno, R. T. Walker, and T. Miyasaka. 1989. Highly specific inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 by a novel 6-substituted acyclouridine derivative. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 165:1375-1381. - PubMed
-
- Buckheit, R. W., Jr. 2004. Understanding HIV resistance, fitness, replication capacity and compensation: targeting viral fitness as a therapeutic strategy. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 13:933-958. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Chemical Information
Medical
Miscellaneous

