Regulation of expression and function of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DP4), DP8/9, and DP10 in allergic responses of the lung in rats
- PMID: 17967935
- PMCID: PMC2324168
- DOI: 10.1369/jhc.7A7319.2007
Regulation of expression and function of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DP4), DP8/9, and DP10 in allergic responses of the lung in rats
Abstract
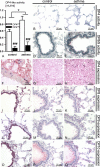
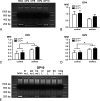
The expression of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DP4, CD26) affects T-cell recruitment to lungs in an experimental rat asthma model. Furthermore, the gene of the structural homologous DP10 represents a susceptibility locus for asthma in humans, and the functional homologous DP8/9 are expressed in human leukocytes. Thus, although several mechanisms may account for a role of DP4-like peptidases in asthma, detailed information on their anatomical sites of expression and function in lungs is lacking. Therefore, bronchi and lung parenchyma were evaluated using immunohistochemistry and histochemical/enzymatic activity assays, as well as quantitative real-time PCR for this family of peptidases in naïve and asthmatic rat lungs derived from wild-type F344 and DP4-deficient F344 rat strains. Surprisingly, results show not only that the induction of experimental asthma increases DP4 enzymatic activity in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and parenchyma, but also that DP8/9 enzymatic activity is regulated and, as well as the expression of DP10, primarily found in the bronchial epithelium of the airways. This is the first report showing a differential and site-specific DP4-like expression and function in the lungs, suggesting a pathophysiologically significant role in asthma.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The effect of CD26-deficiency on dipeptidyl peptidase 8 and 9 expression profiles in a mouse model of Crohn's disease.J Cell Biochem. 2018 Aug;119(8):6743-6755. doi: 10.1002/jcb.26867. Epub 2018 Apr 25. J Cell Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29693275
-
Airway-specific recruitment of T cells is reduced in a CD26-deficient F344 rat substrain.Clin Exp Immunol. 2009 Oct;158(1):133-42. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2009.03991.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19737240 Free PMC article.
-
Expression profiling of dipeptidyl peptidase 8 and 9 in breast and ovarian carcinoma cell lines.Int J Oncol. 2012 Sep;41(3):919-32. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2012.1522. Epub 2012 Jun 19. Int J Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22736146
-
Dipeptidyl peptidase (DP) 6 and DP10: novel brain proteins implicated in human health and disease.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2009;47(3):262-7. doi: 10.1515/cclm.2009.061. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2009. PMID: 19676137 Review.
-
Dipeptidyl peptidase 8 and 9--guilty by association?Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2009 Jan 1;14(10):3619-33. doi: 10.2741/3476. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2009. PMID: 19273298 Review.
Cited by
-
CD26 and Asthma: a Comprehensive Review.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2019 Apr;56(2):139-160. doi: 10.1007/s12016-016-8578-z. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2019. PMID: 27561663 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Paradoxical impairment of angiogenesis, endothelial function and circulating number of endothelial progenitor cells in DPP4-deficient rat after critical limb ischemia.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013 Mar 21;4(2):31. doi: 10.1186/scrt181. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013. PMID: 23517567 Free PMC article.
-
The Dipeptidyl Peptidases 4, 8, and 9 in Mouse Monocytes and Macrophages: DPP8/9 Inhibition Attenuates M1 Macrophage Activation in Mice.Inflammation. 2016 Feb;39(1):413-424. doi: 10.1007/s10753-015-0263-5. Inflammation. 2016. PMID: 26454447
-
Asthma biomarkers in the age of biologics.Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2017 Nov 17;13:48. doi: 10.1186/s13223-017-0219-4. eCollection 2017. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29176991 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The amino terminus extension in the long dipeptidyl peptidase 9 isoform contains a nuclear localization signal targeting the active peptidase to the nucleus.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014 Sep;71(18):3611-26. doi: 10.1007/s00018-014-1591-6. Epub 2014 Feb 23. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 24562348 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbott CA, Yu DM, Woollatt E, Sutherland GR, McCaughan GW, Gorrell MD (2000) Cloning, expression and chromosomal localization of a novel human dipeptidyl peptidase (DPP) IV homolog, DPP8. Eur J Biochem 267:6140–6150 - PubMed
-
- Ajami K, Abbott CA, McCaughan GW, Gorrell MD (2004) Dipeptidyl peptidase 9 has two forms, a broad tissue distribution, cytoplasmic localization and DPIV-like peptidase activity. Biochim Biophys Acta 1679:18–28 - PubMed
-
- Allen M, Heinzmann A, Noguchi E, Abecasis G, Broxholme J, Ponting CP, Bhattacharyya S, et al. (2003) Positional cloning of a novel gene influencing asthma from chromosome 2q14. Nat Genet 35:258–263 - PubMed
-
- Boonacker E, Van Noorden CJ (2003) The multifunctional or moonlighting protein CD26/DPPIV. Eur J Cell Biol 82:53–73 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

