A conserved CaM- and radial spoke associated complex mediates regulation of flagellar dynein activity
- PMID: 17967944
- PMCID: PMC2064796
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200703107
A conserved CaM- and radial spoke associated complex mediates regulation of flagellar dynein activity
Abstract
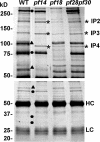
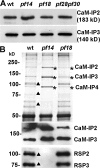
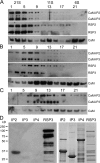
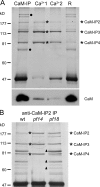
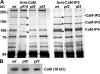
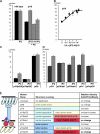
For virtually all cilia and eukaryotic flagella, the second messengers calcium and cyclic adenosine monophosphate are implicated in modulating dynein- driven microtubule sliding to regulate beating. Calmodulin (CaM) localizes to the axoneme and is a key calcium sensor involved in regulating motility. Using immunoprecipitation and mass spectrometry, we identify members of a CaM-containing complex that are involved in regulating dynein activity. This complex includes flagellar-associated protein 91 (FAP91), which shares considerable sequence similarity to AAT-1, a protein originally identified in testis as an A-kinase anchor protein (AKAP)- binding protein. FAP91 directly interacts with radial spoke protein 3 (an AKAP), which is located at the base of the spoke. In a microtubule sliding assay, the addition of antibodies generated against FAP91 to mutant axonemes with reduced dynein activity restores dynein activity to wild-type levels. These combined results indicate that the CaM- and spoke-associated complex mediates regulatory signals between the radial spokes and dynein arms.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The CSC is required for complete radial spoke assembly and wild-type ciliary motility.Mol Biol Cell. 2011 Jul 15;22(14):2520-31. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E11-03-0271. Epub 2011 May 25. Mol Biol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21613541 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Chlamydomonas flagellar dynein by an axonemal protein kinase.J Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;127(6 Pt 1):1683-92. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.6.1683. J Cell Biol. 1994. PMID: 7798320 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of flagellar dynein by an axonemal type-1 phosphatase in Chlamydomonas.J Cell Sci. 1996 Jul;109 ( Pt 7):1899-907. doi: 10.1242/jcs.109.7.1899. J Cell Sci. 1996. PMID: 8832412
-
Keeping an eye on I1: I1 dynein as a model for flagellar dynein assembly and regulation.Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2007 Aug;64(8):569-79. doi: 10.1002/cm.20211. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2007. PMID: 17549744 Review.
-
Functional diversity of axonemal dyneins as studied in Chlamydomonas mutants.Int Rev Cytol. 2002;219:115-55. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(02)19012-7. Int Rev Cytol. 2002. PMID: 12211628 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical detection, diagnosis and treatment of morphological abnormalities of sperm flagella: A review of literature.Front Genet. 2022 Nov 8;13:1034951. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1034951. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36425067 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The eukaryotic flagellum makes the day: novel and unforeseen roles uncovered after post-genomics and proteomics data.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2012 Sep;13(6):524-46. doi: 10.2174/138920312803582951. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2012. PMID: 22708495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The dynein regulatory complex is the nexin link and a major regulatory node in cilia and flagella.J Cell Biol. 2009 Dec 14;187(6):921-33. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200908067. J Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 20008568 Free PMC article.
-
Sequential assembly of flagellar radial spokes.Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2011 Jul;68(7):389-400. doi: 10.1002/cm.20520. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2011. PMID: 21692193 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of Human Airway Cilia Identifies Previously Uncharacterized Proteins of High Abundance.J Proteome Res. 2017 Apr 7;16(4):1579-1592. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.6b00972. Epub 2017 Mar 27. J Proteome Res. 2017. PMID: 28282151 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brokaw, C.J., R. Josslin, and L. Bobrow. 1974. Calcium ion regulation of flagellar beat symmetry in reactivated sea urchin spermatozoa. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 58:795–800. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

