Interactive effects of ethanol and nicotine on learning in C57BL/6J mice depend on both dose and duration of treatment
- PMID: 17968532
- PMCID: PMC2722442
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-007-0982-x
Interactive effects of ethanol and nicotine on learning in C57BL/6J mice depend on both dose and duration of treatment
Abstract
Objective and rationale: Alcohol and nicotine are commonly co-abused; one possible explanation for co-abuse is that each drug ameliorates the aversive effects of the other. Both drugs have dose-dependent effects on learning and memory. Thus, this study examined the interactive effects of acute ethanol and acute, chronic, or withdrawal from chronic nicotine on fear conditioning in C57BL/6J mice.
Materials and methods: Conditioning consisted of auditory conditioned stimulus-foot-shock unconditioned stimulus pairings. For acute studies, saline or ethanol, then saline or nicotine was administered before training, and saline or nicotine was also administered before testing. For chronic and withdrawal studies, saline or nicotine was administered chronically, and ethanol or saline was administered before training.
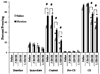
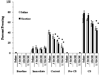
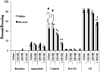
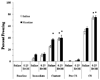
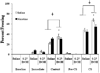
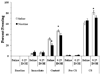
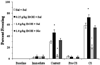
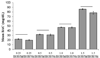
Results: Acute nicotine (0.09 mg/kg) reversed ethanol-induced deficits (1.0 and 1.5 g/kg) in contextual and cued fear conditioning, whereas a low dose of ethanol (0.25 g/kg) reversed nicotine (6.3 mg kg(-1) day(-1)) withdrawal-induced deficits in contextual conditioning. Tolerance developed for the effects of nicotine on ethanol-induced deficits in conditioning and cross-tolerance between chronic nicotine and acute ethanol was seen for the enhancing effects of ethanol on conditioning.
Conclusions: The complex and sometimes polar actions of ethanol and nicotine on behavior may contribute to co-abuse of these drugs. Specifically, smoking may initially reduce the aversive effects of ethanol, but tolerance develops for this effect. In addition, low doses of alcohol may lessen nicotine withdrawal symptoms.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The hippocampus and cingulate cortex differentially mediate the effects of nicotine on learning versus on ethanol-induced learning deficits through different effects at nicotinic receptors.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2009 Aug;34(9):2167-79. doi: 10.1038/npp.2009.45. Epub 2009 Apr 29. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2009. PMID: 19404242 Free PMC article.
-
Nicotine enhances contextual fear conditioning and ameliorates ethanol-induced deficits in contextual fear conditioning.Behav Neurosci. 2003 Dec;117(6):1276-82. doi: 10.1037/0735-7044.117.6.1276. Behav Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 14674846
-
The effects of galantamine on nicotine withdrawal-induced deficits in contextual fear conditioning in C57BL/6 mice.Behav Brain Res. 2011 Sep 30;223(1):53-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2011.04.010. Epub 2011 Apr 14. Behav Brain Res. 2011. PMID: 21514327 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of nicotine in experimental animals and humans: an update on addictive properties.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2009;(192):335-67. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-69248-5_12. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19184655 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alterations in the levels of heterotrimeric G protein subunits induced by psychostimulants, opiates, barbiturates, and ethanol: Implications for drug dependence, tolerance, and withdrawal.Synapse. 2008 Sep;62(9):689-99. doi: 10.1002/syn.20543. Synapse. 2008. PMID: 18566973 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of drugs of abuse on hippocampal plasticity and hippocampus-dependent learning and memory: contributions to development and maintenance of addiction.Learn Mem. 2016 Sep 15;23(10):515-33. doi: 10.1101/lm.042192.116. Print 2016 Oct. Learn Mem. 2016. PMID: 27634143 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Negative affective states and cognitive impairments in nicotine dependence.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2015 Nov;58:168-85. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2015.06.004. Epub 2015 Jun 6. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2015. PMID: 26054790 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of ethanol and caffeine on behavior in C57BL/6 mice in the plus-maze discriminative avoidance task.Behav Neurosci. 2009 Dec;123(6):1271-8. doi: 10.1037/a0017610. Behav Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 20001110 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of hippocampus-dependent learning and synaptic plasticity by nicotine.Mol Neurobiol. 2008 Aug;38(1):101-21. doi: 10.1007/s12035-008-8037-9. Epub 2008 Aug 9. Mol Neurobiol. 2008. PMID: 18690555 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The genetic components of alcohol and nicotine co-addiction: from genes to behavior.Curr Drug Abuse Rev. 2008 Jun;1(2):124-34. doi: 10.2174/1874473710801020124. Curr Drug Abuse Rev. 2008. PMID: 19492010 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alkondon M, Albuquerque EX. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor a7 and a4b2 subtypes differentially control GABAergic input to CA1 neurons in rat hippocampus. J Neurophys. 2001;86:3043–3055. - PubMed
-
- Bammer G, Chesher GB. An analysis of some effects of ethanol on performance in a passive avoidance task. Psychopharmacology. 1982;77:66–73. - PubMed
-
- Bowers BJ, McClure-Begley TD, Keller JJ, Paylor R, Collins AC, Wehner JM. Deletion of the α7 nicotinic receptor subunit gene results in increased sensitivity to several behavioral effects produced by alcohol. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2005;29(3):295–302. - PubMed
-
- Celerier A, Ognard R, Decorte L, Beracochea D. Deficits of spatial and non-spatial memory and of auditory fear conditioning following anterior thalamic lesions in mice: comparison with chronic alcohol consumption. Eur J Neurosci. 2000;12:2575–2584. - PubMed
-
- Chen WJ, Parnell SE, West JR. Nicotine decreases blood alcohol concentration in neonatal rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2001;23(1):18–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

