Deletion of the STOP gene, a microtubule stabilizing factor, leads only to discrete cerebral metabolic changes in mice
- PMID: 17969102
- PMCID: PMC2702481
- DOI: 10.1002/jnr.21550
Deletion of the STOP gene, a microtubule stabilizing factor, leads only to discrete cerebral metabolic changes in mice
Abstract
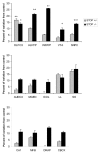
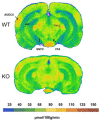
In mice, deletion of the STOP protein leads to subtle anatomic changes and induces depleted synaptic vesicle pools, impaired synaptic plasticity, hyperdopaminergy, and major behavioral disorders alleviated by neuroleptics, hence leading to a schizophrenic-like phenotype. In this study, we applied the quantitative autoradiographic [(14)C]2-deoxyglucose technique to study to what extent the basal rate of cerebral glucose utilization in STOP-knockout (STOP-KO) mice occurs in regions where metabolic changes have been reported in schizophrenic patients. Studies were performed on wild-type, heterozygous, and homozygous STOP-KO mice (7-8 per group). Mice were implanted with femoral artery and vein catheters, and cerebral glucose utilization was quantified over 45 min. Compared with that in wild-type mice, glucose utilization in STOP-KO mice was significantly increased in the olfactory cortex, ventromedial and anterolateral hypothalamus, ventral tegmental area, and substantia nigra pars compacta. Nonsignificant increases, ranging between 9% and 19%, were recorded in the whole auditory system, CA1 pyramidal cell layer, and dorsal raphe. Glucose utilization was also significantly increased in heterozygous mice compared with that in wild-type mice in olfactory cortex. These data might reflect hyperdopaminergic activity, olfactory deficits, and sleep disturbances in STOP-KO mice that have also been reported in schizophrenic patients.
(c) 2007 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hypoglutamatergic activity in the STOP knockout mouse: a potential model for chronic untreated schizophrenia.J Neurosci Res. 2007 Nov 15;85(15):3487-93. doi: 10.1002/jnr.21200. J Neurosci Res. 2007. PMID: 17304567
-
Olfactory bulbectomy reduces cerebral glucose utilization: 2-[14C]deoxyglucose autoradiographic study.Brain Res Bull. 2008 Jul 30;76(5):485-92. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2008.01.020. Epub 2008 Feb 20. Brain Res Bull. 2008. PMID: 18534256
-
Altered expression of synaptic protein mRNAs in STOP (MAP6) mutant mice.J Psychopharmacol. 2007 Aug;21(6):635-44. doi: 10.1177/0269881106068825. Epub 2006 Oct 18. J Psychopharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17050659
-
Principles of the 2-deoxyglucose method for the determination of the local cerebral glucose utilization.Eur J Morphol. 1990;28(2-4):132-8. Eur J Morphol. 1990. PMID: 2245129 Review.
-
The determination of the local cerebral glucose utilization with the 2-deoxyglucose method.Histochemistry. 1988;90(2):109-21. doi: 10.1007/BF00500975. Histochemistry. 1988. PMID: 3068213 Review.
Cited by
-
Caffeine-Induced Acute and Delayed Responses in Cerebral Metabolism of Control and Schizophrenia-Like Wisket Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 25;23(15):8186. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158186. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35897774 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocyte Bioenergetics and Major Psychiatric Disorders.Adv Neurobiol. 2021;26:173-227. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-77375-5_9. Adv Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 34888836 Review.
-
Disruptions of Sleep/Wake Patterns in the Stable Tubule Only Polypeptide (STOP) Null Mouse Model of Schizophrenia.Schizophr Bull. 2016 Sep;42(5):1207-15. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbw017. Epub 2016 Mar 2. Schizophr Bull. 2016. PMID: 26940700 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abi-Dargham A, Gil R, Krystal J, Baldwin BM, Seibyl JP, Bowers M, van Dyck CH, Charney DS, Innis RB, Laruelle M. Increased striatal dopamine transmission in schizophrenia: confirmation in a second cohort. Am J Psychiatry. 1998;155:761–767. - PubMed
-
- Aleman A, Bocker KB, Hijman R, de Haan EH, Kahn RS. Cognitive basis of hallucinations in schizophrenia: role of top-down information processing. Schizophr Res. 2003;64:175–185. - PubMed
-
- Andreasen NC, Black DW. Introductory Textbook of Psychiatry. American Psychiatry Press; Washington, DC: 1991.
-
- Andrieux A, Salin PA, Vernet M, Kujala P, Baratier J, Gory-Fauré S, Bosc C, Pointu H, Proietto D, Schweitzer A, Denarier E, Klumperman J, Job D. The suppression of brain cold-stable microtubules in mice induces synaptic defects associated with neuroleptic-sensitive behavioral disorders. Genes Dev. 2002;16:2350–2364. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andrieux A, Salin P, Schweitzer A, Begou M, Pachoud B, Brun P, Gory-Faure S, Kujala P, Suaud-Chagny MF, Höfle G, Job D. Microtubule stabilizer ameliorates synaptic function and behavior in a mouse model for schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry. 2006;60:1224–1230. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

