Ambulatory blood pressure in hypertensive patients with left ventricular hypertrophy: efficacy of first-line combination perindopril/indapamide therapy
- PMID: 17969366
- PMCID: PMC2291338
Ambulatory blood pressure in hypertensive patients with left ventricular hypertrophy: efficacy of first-line combination perindopril/indapamide therapy
Abstract
Background: Ambulatory blood pressure (BP) is more sensitive than office BP and is highly correlated with the left ventricular mass (LVM) of hypertensive patients with left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH).
Methods: In this prospectively designed ancillary study of the PICXEL trial, the effects of first-line combination perindopril/indapamide on ambulatory BP were compared with those of monotherapy with enalapril in 127 patients. Hypertensive patients with LVH received once daily either perindopril 2 mg/indapamide 0.625 mg (n = 65) or enalapril 10 mg (n = 62) for 52 weeks. Dose adjustments were allowed for uncontrolled BP. Twenty-four-hour ambulatory BP and echocardiographic parameters were measured at baseline, week 24, and week 52.
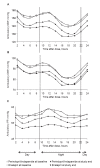
Results: At study end, both treatments significantly improved ambulatory BP compared with baseline (p < or = 0.01). Perindopril/indapamide treatment reduced 24-hour and daytime systolic BP (SBP) and pulse pressure (PP) significantly more than enalapril treatment (p < 0.01). No significant between-group differences were noted for diastolic BP (DBP) or for night-time measurements. Trough/peak ratios were higher with perindopril/indapamide than with enalapril (88.5 vs 65.8 for SBP and 86.7 vs 63.9 for DBP, respectively). The global smoothness index was higher with perindopril/indapamide than with enalapril (6.6 vs 5.2 for SBP and 5.6 vs 4.9 for DBP, respectively). With perindopril/indapamide treatment, LVM index was significantly reduced (-9.1 g/m2 from baseline; p vs baseline <0.001). More patients required dose increases with enalapril (87%) than with perindopril/indapamide (71%). No unusual safety elements were noted.
Conclusions: First-line perindopril/indapamide combination decreased ambulatory SBP and PP, and LVM more effectively than enalapril.
Figures



References
-
- Meta-analysis suggests regression of left ventricular hypertrophy during antihypertensive treatment is linked to reduced risk of cardiovascular disease. Evid Based Cardiovasc Med. 2004;8:22–3. - PubMed
-
- Bobrie G, Delonca J, Moulin C, et al. A home blood pressure monitoring study comparing the antihypertensive efficacy of two angiotensin II receptor antagonist fixed combinations. Am J Hypertens. 2005;18:1482–8. - PubMed
-
- Casale PN, Devereux RB, Milner M, et al. Value of echocardiographic measurement of left ventricular mass in predicting cardiovascular morbid events in hypertensive men. Ann Intern Med. 1986;105:173–8. - PubMed
-
- Chalmers J, Castaigne A, Morgan T, et al. Long-term efficacy of a new, fixed, very-low-dose angiotensin-converting enzyme-inhibitor/diuretic combination as first-line therapy in elderly hypertensive patients. J Hypertens. 2000;18:327–37. - PubMed
-
- Chanudet X, de Champvallins M. Antihypertensive efficacy and tolerability of low-dose perindopril/indapamide combination compared with losartan in the treatment of essential hypertension. Int J Clin Pract. 2001;55:233–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

