Drug targets in mycobacterial sulfur metabolism
- PMID: 17970225
- PMCID: PMC3106421
- DOI: 10.2174/187152607781001772
Drug targets in mycobacterial sulfur metabolism
Abstract
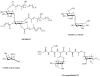
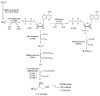
The identification of new antibacterial targets is urgently needed to address multidrug resistant and latent tuberculosis infection. Sulfur metabolic pathways are essential for survival and the expression of virulence in many pathogenic bacteria, including Mycobacterium tuberculosis. In addition, microbial sulfur metabolic pathways are largely absent in humans and therefore, represent unique targets for therapeutic intervention. In this review, we summarize our current understanding of the enzymes associated with the production of sulfated and reduced sulfur-containing metabolites in Mycobacteria. Small molecule inhibitors of these catalysts represent valuable chemical tools that can be used to investigate the role of sulfur metabolism throughout the Mycobacterial lifecycle and may also represent new leads for drug development. In this light, we also summarize recent progress in the development of inhibitors of sulfur metabolism enzymes.
Figures

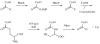

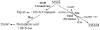
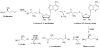
References
-
- Corbett EL, Watt CJ, Walker N, Maher D, Williams BG, Raviglione MC, Dye C. Arch Intern Med. 2003;163:1009. - PubMed
-
- Dye C, Scheele S, Dolin P, Pathania V, Raviglione MC. JAMA. 1999;282:677. - PubMed
-
- Blumberg HM, Burman WJ, Chaisson RE, Daley CL, Etkind SC, Friedman LN, Fujiwara P, Grzemska M, Hopewell PC, Iseman MD, Jasmer RM, Koppaka V, Menzies RI, O’Brien RJ, Reves RR, Reichman LB, Simone PM, Starke JR, Vernon AA. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003;167:603. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2005;45:529. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
