New concepts in antimalarial use and mode of action in dermatology
- PMID: 17970883
- PMCID: PMC7163426
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1529-8019.2007.00131.x
New concepts in antimalarial use and mode of action in dermatology
Abstract
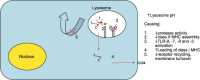
Although chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine and quinacrine were originally developed for the treatment of malaria, these medications have been used to treat skin disease for over 50 years. Recent clinical data have confirmed the usefulness of these medications for the treatment of lupus erythematosus. Current research has further enhanced our understanding of the pharmacologic mechanisms of action of these drugs involving inhibition of endosomal toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling limiting B cell and dendritic cell activation. With this understanding, the use of these medications in dermatology is broadening. This article highlights the different antimalarials used within dermatology through their pharmacologic properties and mechanism of action, as well as indicating their clinical uses. In addition, contraindications, adverse effects, and possible drug interactions of antimalarials are reviewed.
Figures

References
-
- Ruiz‐Irastorza G, Egurbide MV, Pijoan JI, et al Effect of antimalarials on thrombosis and survival in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 2006: 15: 577. - PubMed
-
- Payne JF. A postgraduate lecture on lupus erythematosus. Clin J 1894: 4: 223–229.
-
- Isaacson D, Elgart M, Turner ML. Anti‐malarials in dermatology. Int J Dermatol 1982: 21: 379–395. - PubMed
-
- Hofheniz W, Merkli B. Quinine and quinine analogues In: Peters W, Richards WHG, eds. Antimalarial drugs II: current antimalarials and new drug development. New York: Springer‐Verlag, 1984: 61.
-
- Page F. Treatment of lupus erythematosus with mepacrine. Lancet 1951: 2: 755–758. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

