Association of fewer hours of sleep at 6 months postpartum with substantial weight retention at 1 year postpartum
- PMID: 17971337
- PMCID: PMC2930882
- DOI: 10.1093/aje/kwm298
Association of fewer hours of sleep at 6 months postpartum with substantial weight retention at 1 year postpartum
Abstract
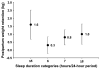
Shorter sleep duration is linked to obesity, coronary artery disease, and diabetes. Whether sleep deprivation during the postpartum period affects maternal postpartum weight retention remains unknown. This study examined the association of sleep at 6 months postpartum with substantial postpartum weight retention (SPPWR), defined as 5 kg or more above pregravid weight at 1 year postpartum. The authors selected 940 participants in Project Viva who enrolled during early pregnancy from 1999 to 2002. Logistic regression models estimated odds ratios of SPPWR for sleep categories, controlling for sociodemographic, prenatal, and behavioral attributes. Of the 940 women, 124 (13%) developed SPPWR. Sleep distributions were as follows: 114 (12%) women slept < or =5 hours/day, 280 (30%) slept 6 hours/day, 321 (34%) slept 7 hours/day, and 225 (24%) slept > or =8 hours/day. Adjusted odds ratios of SPPWR were 3.13 (95% confidence interval (CI): 1.42, 6.94) for < or =5 hours/day, 0.99 (95% CI: 0.50, 1.97) for 6 hours/day, and 0.94 (95% CI: 0.50, 1.78) for > or =8 hours/day versus 7 hours/day (p = 0.012). The adjusted odds ratio for SPPWR of 2.05 (95% CI: 1.11, 3.78) was twofold greater (p = 0.02) for a decrease in versus no change in sleep at 1 year postpartum. Sleeping < or =5 hours/day at 6 months postpartum was strongly associated with retaining > or =5 kg at 1 year postpartum. Interventions to prevent postpartum obesity should consider strategies to attain optimal maternal sleep duration.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Associations of maternal material hardships during childhood and adulthood with prepregnancy weight, gestational weight gain, and postpartum weight retention.J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2015 Jul;24(7):563-71. doi: 10.1089/jwh.2014.5016. Epub 2015 Apr 22. J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2015. PMID: 25902486 Free PMC article.
-
The association between gestational weight gain and substantial weight retention 1-year postpartum.Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2014 Sep;290(3):493-9. doi: 10.1007/s00404-014-3235-3. Epub 2014 Apr 12. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2014. PMID: 24728106
-
Risk factors for substantial weight retention at 1 year postpartum: evidence from a German birth cohort study (KUNO-Kids).Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2025 Apr;311(4):997-1006. doi: 10.1007/s00404-024-07795-6. Epub 2024 Nov 27. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2025. PMID: 39592472 Free PMC article.
-
[Determinant factors of postpartum weight retention: a literature review].Cad Saude Publica. 2001 May-Jun;17(3):455-66. doi: 10.1590/s0102-311x2001000300002. Cad Saude Publica. 2001. PMID: 11395784 Review. Portuguese.
-
Weight change in the postpartum period. A review of the literature.J Nurse Midwifery. 1995 Sep-Oct;40(5):418-23. doi: 10.1016/0091-2182(95)00049-p. J Nurse Midwifery. 1995. PMID: 7472647 Review.
Cited by
-
Determinants of excessive gestational weight gain in urban, low-income women.Womens Health Issues. 2012 Sep;22(5):e439-46. doi: 10.1016/j.whi.2012.05.004. Epub 2012 Jul 17. Womens Health Issues. 2012. PMID: 22818249 Free PMC article.
-
Association between sleep deficiency and cardiometabolic disease: implications for health disparities.Sleep Med. 2016 Feb;18:19-35. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2015.02.535. Epub 2015 Mar 23. Sleep Med. 2016. PMID: 26431758 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sleep duration and cardiometabolic risk: a review of the epidemiologic evidence.Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010 Oct;24(5):731-43. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2010.07.001. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010. PMID: 21112022 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The relationship between breastfeeding and postpartum weight change--a systematic review and critical evaluation.Int J Obes (Lond). 2014 Apr;38(4):577-90. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2013.132. Epub 2013 Jul 29. Int J Obes (Lond). 2014. PMID: 23892523
-
Postpartum screening for diabetes among women with a history of gestational diabetes mellitus.Prev Chronic Dis. 2011 Nov;8(6):A124. Epub 2011 Oct 17. Prev Chronic Dis. 2011. PMID: 22005617 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kripke DF, Garfinkel L, Wingard DL, et al. Mortality associated with sleep duration and insomnia. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2002;59:131–6. - PubMed
-
- Patel SR, Ayas NT, Malhotra MR, et al. A prospective study of sleep duration and mortality risk in women. Sleep. 2004;27:440–4. - PubMed
-
- Flier JS, Elmquist JK. A good night's sleep: future antidote to the obesity epidemic? Ann Intern Med. 2004;141:885–6. - PubMed
-
- Gangwisch JE, Malaspina D, Boden-Albala B, et al. Inadequate sleep as a risk factor for obesity: analyses of the NHANES I. Sleep. 2005;28:1289–96. - PubMed
-
- Hasler G, Buysse DJ, Klaghofer R, et al. The association between short sleep duration and obesity in young adults: a 13-year prospective study. Sleep. 2004;27:661–6. - PubMed