Prazosin displays anticancer activity against human prostate cancers: targeting DNA and cell cycle
- PMID: 17971903
- PMCID: PMC2040210
- DOI: 10.1593/neo.07475
Prazosin displays anticancer activity against human prostate cancers: targeting DNA and cell cycle
Abstract
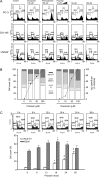
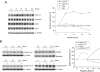
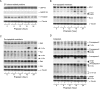
Quinazoline-based alpha1-adrenoceptor antagonists, in particular doxazosin and terazosin, are suggested to display antineoplastic activity against prostate cancers. However, there are few studies elucidating the effect of prazosin. In this study, prazosin displayed antiproliferative activity superior to that of other alpha1-blockers, including doxazosin, terazosin, tamsulosin, and phentolamine. Prazosin induced G2 checkpoint arrest and subsequent apoptosis in prostate cancer PC-3, DU-145, and LNCaP cells. In p53-null PC-3 cells, prazosin induced an increase in DNA strand breaks and ATM/ATR checkpoint pathways, leading to the activation of downstream signaling cascades, including Cdc25c phosphorylation at Ser216, nuclear export of Cdc25c, and cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) 1 phosphorylation at Tyr15. The data, together with sustained elevated cyclin A levels (other than cyclin B1 levels), suggested that Cdk1 activity was inactivated by prazosin. Moreover, prazosin triggered mitochondria-mediated and caspase-executed apoptotic pathways in PC-3 cells. The oral administration of prazosin significantly reduced tumor mass in PC-3-derived cancer xenografts in nude mice. In summary, we suggest that prazosin is a potential antitumor agent that induces cell apoptosis through the induction of DNA damage stress, leading to Cdk1 inactivation and G2 checkpoint arrest. Subsequently, mitochondria-mediated caspase cascades are triggered to induce apoptosis in PC-3 cells.
Keywords: Cdc25c; DNA damage; Prazosin; cell cycle; mitochondria-involved apoptosis.
Figures

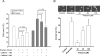
Similar articles
-
Suppression of human prostate cancer cell growth by alpha1-adrenoceptor antagonists doxazosin and terazosin via induction of apoptosis.Cancer Res. 2000 Aug 15;60(16):4550-5. Cancer Res. 2000. PMID: 10969806
-
Relative cytotoxic potencies and cell death mechanisms of α1 -adrenoceptor antagonists in prostate cancer cell lines.Prostate. 2016 Jun;76(8):757-66. doi: 10.1002/pros.23167. Epub 2016 Feb 16. Prostate. 2016. PMID: 26880388
-
Anoikis induction by quinazoline based alpha 1-adrenoceptor antagonists in prostate cancer cells: antagonistic effect of bcl-2.J Urol. 2003 Mar;169(3):1150-6. doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000042453.12079.77. J Urol. 2003. PMID: 12576871
-
Apoptotic impact of alpha1-blockers on prostate cancer growth: a myth or an inviting reality?Prostate. 2004 Apr 1;59(1):91-100. doi: 10.1002/pros.10357. Prostate. 2004. PMID: 14991869 Review.
-
The Role of α1-Adrenoceptor Antagonists in the Treatment of Prostate and Other Cancers.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Aug 16;17(8):1339. doi: 10.3390/ijms17081339. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27537875 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Overcoming Drug Resistance in Advanced Prostate Cancer by Drug Repurposing.Med Sci (Basel). 2022 Feb 18;10(1):15. doi: 10.3390/medsci10010015. Med Sci (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35225948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
First small-molecule PROTACs for G protein-coupled receptors: inducing α 1A-adrenergic receptor degradation.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2020 Sep;10(9):1669-1679. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.01.014. Epub 2020 Jan 27. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2020. PMID: 33088687 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of novel p53 pathway activating small-molecule compounds reveals unexpected similarities with known therapeutic agents.PLoS One. 2010 Sep 27;5(9):e12996. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012996. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20885994 Free PMC article.
-
Denbinobin induces apoptosis by apoptosis-inducing factor releasing and DNA damage in human colorectal cancer HCT-116 cells.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2008 Nov;378(5):447-57. doi: 10.1007/s00210-008-0324-5. Epub 2008 Jul 8. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18607570
-
The War on Cancer rages on.Neoplasia. 2009 Dec;11(12):1252-63. doi: 10.1593/neo.91866. Neoplasia. 2009. PMID: 20019833 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kyprianou N, English HF, Isaacs JT. Programmed cell death during regression of PC-82 human prostate cancer following androgen ablation. Cancer Res. 1990;50:3748–3753. - PubMed
-
- Efstathiou E, Bozas G, Kostakopoulos A, Kastritis E, Deliveliotis C, Antoniou N, Skarlos D, Papadimitriou C, Dimopoulos MA, Bamias A. Combination of docetaxel, estramustine phosphate, and zoledronic acid in androgen-independent metastatic prostate cancer: efficacy, safety, and clinical benefit assessment. Urology. 2005;65:126–130. - PubMed
-
- Martel CL, Gumerlock PH, Meyers FJ, Lara PN. Current strategies in the management of hormone refractory prostate cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 2003;29:171–187. - PubMed
-
- Angelucci A, Valentini A, Millimaggi D, Gravina GL, Miano R, Dolo V, Vicentini C, Bologna M, Federici G, Bernardini S. Valproic acid induces apoptosis in prostate carcinoma cell lines by activation of multiple death pathways. Anticancer Drugs. 2006;17:1141–1150. - PubMed
-
- Chiang PC, Kung FL, Huang DM, Li TK, Fan JR, Pan SL, Shen YC, Guh JH. Induction of Fas clustering and apoptosis by coral prostanoid in human hormone-resistant prostate cancer cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 2006;542:22–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
