Aggrecan, versican and type VI collagen are components of annular translamellar crossbridges in the intervertebral disc
- PMID: 17972112
- PMCID: PMC2365556
- DOI: 10.1007/s00586-007-0538-0
Aggrecan, versican and type VI collagen are components of annular translamellar crossbridges in the intervertebral disc
Abstract
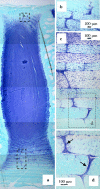
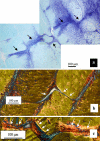
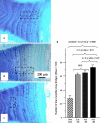
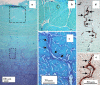
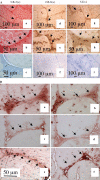
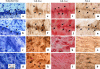
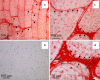
The aim of this study was to undertake a detailed analysis of the structure of the inter and intra-lamellar regions of the annulus fibrosus. A total of 30 newborn to 6 year-old lumbar ovine intervertebral discs (IVDs) were fixed and decalcified en-bloc to avoid differential swelling artifacts during processing and vertical mid-sagittal, and horizontal 4 mum sections were cut. These were stained with toluidine blue to visualise anionic proteoglycan (PG) species, H & E for cellular morphology and picro-sirius red (viewed under polarized light) to examine collagenous organization. Immunolocalisations were also undertaken using anti-PG core-protein and glycosaminoglycan (GAG) side chain antibodies to native chondroitin sulphate (CS), Delta C-4-S and C-6-S unsaturated stubs generated by chondroitinase ABC digestion of CS, keratan sulphate (KS), and with antibodies to type I, II, VI, IX and X collagens. Trans-lamellar cross bridges (TLCBs), discontinuities in annular lamellae's which provide transverse interconnections, stained prominently with toluidine blue in the adult IVDs but less so in the newborn IVDs. In adult discs TLCBs were evident in both the posterior and anterior AF where they extended from the outermost annular lamellae almost to the transitional zone extending across as many as eight lamellar layers displaying a characteristic circuitous, meandering, serpentine type course. There were significantly fewer TLCBs in 2 week-old compared with skeletally mature sheep and there was a further increase from 2 to 6 years. Immunolocalisation of perlecan delineated blood vessels in the TLBs of the newborn but not adult IVDs extending into the mid AF. In contrast adult but not 2 week-old TLCBs were immunopositive for C-4-S, C-6-S, KS, aggrecan, versican and type VI collagen. The change in number and matrix components of the trans-lamellar cross bridges with skeletal maturity and ageing suggest that they represent an adaptation to the complex biomechanical forces occurring in the annulus fibrosus.
Figures

References
-
- Buckwalter JA. Aging and degeneration of the human intervertebral disc. Spine. 1995;20:1307–1314. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

