Biosynthetic tailoring of microcin E492m: post-translational modification affords an antibacterial siderophore-peptide conjugate
- PMID: 17973380
- PMCID: PMC2522288
- DOI: 10.1021/ja074650f
Biosynthetic tailoring of microcin E492m: post-translational modification affords an antibacterial siderophore-peptide conjugate
Abstract
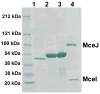
The present work reveals that four proteins, MceCDIJ, encoded by the MccE492 gene cluster are responsible for the remarkable post-translational tailoring of microcin E492 (MccE492), an 84-residue protein toxin secreted by Klebsiella pneumonaie RYC492 that targets neighboring Gram-negative species. This modification results in attachment of a linearized and monoglycosylated derivative of enterobactin, a nonribosomal peptide and iron scavenger (siderophore), to the MccE492m C-terminus. MceC and MceD derivatize enterobactin by C-glycosylation at the C5 position of a N-(2,3-dihydroxybenzoyl)serine (DHB-Ser) moiety and regiospecific hydrolysis of an ester linkage in the trilactone scaffold, respectively. MceI and MceJ form a protein complex that attaches C-glycosylated enterobactins to the C-terminal serine residue of both a C10 model peptide and full-length MccE492. In the enzymatic product, the C-terminal serine residue is covalently attached to the C4' oxygen of the glucose moiety. Nonenzymatic and base-catalyzed migration of the peptide to the C6' position affords the C6' glycosyl ester linkage observed in the mature toxin, MccE492m, isolated from bacterial cultures.
Figures
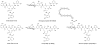




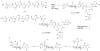

Similar articles
-
Investigations of the MceIJ-catalyzed posttranslational modification of the microcin E492 C-terminus: linkage of ribosomal and nonribosomal peptides to form "trojan horse" antibiotics.Biochemistry. 2008 Sep 2;47(35):9289-99. doi: 10.1021/bi800826j. Epub 2008 Aug 9. Biochemistry. 2008. PMID: 18690711
-
Parasitism of iron-siderophore receptors of Escherichia coli by the siderophore-peptide microcin E492m and its unmodified counterpart.Biometals. 2006 Apr;19(2):181-91. doi: 10.1007/s10534-005-4452-9. Biometals. 2006. PMID: 16718603 Review.
-
Siderophore peptide, a new type of post-translationally modified antibacterial peptide with potent activity.J Biol Chem. 2004 Jul 2;279(27):28233-42. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M400228200. Epub 2004 Apr 21. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15102848
-
Insight into siderophore-carrying peptide biosynthesis: enterobactin is a precursor for microcin E492 posttranslational modification.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007 Oct;51(10):3546-53. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00261-07. Epub 2007 Jul 23. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007. PMID: 17646411 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial and antitumorigenic properties of microcin E492, a pore-forming bacteriocin.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2009 Jan;10(1):74-85. doi: 10.2174/138920109787048643. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2009. PMID: 19149591 Review.
Cited by
-
Isolation and characterization of two members of the siderophore-microcin family, microcins M and H47.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010 Jan;54(1):288-97. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00744-09. Epub 2009 Nov 2. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010. PMID: 19884380 Free PMC article.
-
Natural products as mediators of disease.Nat Prod Rep. 2017 Feb 1;34(2):194-219. doi: 10.1039/c6np00063k. Epub 2016 Nov 22. Nat Prod Rep. 2017. PMID: 27874907 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Revisiting the Multifaceted Roles of Bacteriocins : The Multifaceted Roles of Bacteriocins.Microb Ecol. 2024 Feb 14;87(1):41. doi: 10.1007/s00248-024-02357-4. Microb Ecol. 2024. PMID: 38351266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The production in vivo of microcin E492 with antibacterial activity depends on salmochelin and EntF.J Bacteriol. 2008 Aug;190(15):5464-71. doi: 10.1128/JB.00351-08. Epub 2008 May 23. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 18502859 Free PMC article.
-
Syntheses of Siderophore-Drug Conjugates Using a Convergent Thiol-Maleimide System.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2012 Oct 11;3(10):799-803. doi: 10.1021/ml300150y. Epub 2012 Sep 4. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2012. PMID: 23264853 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Duquesne S, Destoumieux-Garzón D, Peduzzi J, Rebuffat S. Nat Prod Rep. 2007;24:708–734. - PubMed
-
- Pons AM, Lanneluc I, Cottenceau G, Sable S. Biochimie. 2002;84:531–537. - PubMed
-
- Heddle JG, Blance SJ, Zamble DB, Hollfelder F, Miller DA, Wentzell LM, Walsh CT, Maxwell A. J Mol Biol. 2001;307:1223–1234. - PubMed
-
- Metlitskaya A, Kazakov T, Kommer A, Pavlova O, Praetorius-Ibba M, Ibba M, Krasheninnikov I, Kolb V, Khmel I, Severinov K. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:18033–18042. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

