Biosynthetic tailoring of microcin E492m: post-translational modification affords an antibacterial siderophore-peptide conjugate
- PMID: 17973380
- PMCID: PMC2522288
- DOI: 10.1021/ja074650f
Biosynthetic tailoring of microcin E492m: post-translational modification affords an antibacterial siderophore-peptide conjugate
Abstract
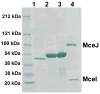
The present work reveals that four proteins, MceCDIJ, encoded by the MccE492 gene cluster are responsible for the remarkable post-translational tailoring of microcin E492 (MccE492), an 84-residue protein toxin secreted by Klebsiella pneumonaie RYC492 that targets neighboring Gram-negative species. This modification results in attachment of a linearized and monoglycosylated derivative of enterobactin, a nonribosomal peptide and iron scavenger (siderophore), to the MccE492m C-terminus. MceC and MceD derivatize enterobactin by C-glycosylation at the C5 position of a N-(2,3-dihydroxybenzoyl)serine (DHB-Ser) moiety and regiospecific hydrolysis of an ester linkage in the trilactone scaffold, respectively. MceI and MceJ form a protein complex that attaches C-glycosylated enterobactins to the C-terminal serine residue of both a C10 model peptide and full-length MccE492. In the enzymatic product, the C-terminal serine residue is covalently attached to the C4' oxygen of the glucose moiety. Nonenzymatic and base-catalyzed migration of the peptide to the C6' position affords the C6' glycosyl ester linkage observed in the mature toxin, MccE492m, isolated from bacterial cultures.
Figures
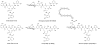




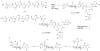

References
-
- Duquesne S, Destoumieux-Garzón D, Peduzzi J, Rebuffat S. Nat Prod Rep. 2007;24:708–734. - PubMed
-
- Pons AM, Lanneluc I, Cottenceau G, Sable S. Biochimie. 2002;84:531–537. - PubMed
-
- Heddle JG, Blance SJ, Zamble DB, Hollfelder F, Miller DA, Wentzell LM, Walsh CT, Maxwell A. J Mol Biol. 2001;307:1223–1234. - PubMed
-
- Metlitskaya A, Kazakov T, Kommer A, Pavlova O, Praetorius-Ibba M, Ibba M, Krasheninnikov I, Kolb V, Khmel I, Severinov K. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:18033–18042. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

