Translation initiation region sequence preferences in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 17973990
- PMCID: PMC2176067
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2199-8-100
Translation initiation region sequence preferences in Escherichia coli
Abstract
Background: The mRNA translation initiation region (TIR) comprises the initiator codon, Shine-Dalgarno (SD) sequence and translational enhancers. Probably the most abundant class of enhancers contains A/U-rich sequences. We have tested the influence of SD sequence length and the presence of enhancers on the efficiency of translation initiation.
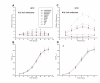
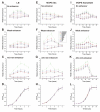
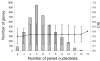
Results: We found that during bacterial growth at 37 degrees C, a six-nucleotide SD (AGGAGG) is more efficient than shorter or longer sequences. The A/U-rich enhancer contributes strongly to the efficiency of initiation, having the greatest stimulatory effect in the exponential growth phase of the bacteria. The SD sequences and the A/U-rich enhancer stimulate translation co-operatively: strong SDs are stimulated by the enhancer much more than weak SDs. The bacterial growth rate does not have a major influence on the TIR selection pattern. On the other hand, temperature affects the TIR preference pattern: shorter SD sequences are preferred at lower growth temperatures. We also performed an in silico analysis of the TIRs in all E. coli mRNAs. The base pairing potential of the SD sequences does not correlate with the codon adaptation index, which is used as an estimate of gene expression level.
Conclusion: In E. coli the SD selection preferences are influenced by the growth temperature and not influenced by the growth rate. The A/U rich enhancers stimulate translation considerably by acting co-operatively with the SD sequences.
Figures

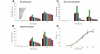
Similar articles
-
Epsilon as an initiator of translation of CAT mRNA in Escherichia coli.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000 Jul 5;273(2):528-31. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2000.2958. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000. PMID: 10873639
-
How Changes in Anti-SD Sequences Would Affect SD Sequences in Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis.G3 (Bethesda). 2017 May 5;7(5):1607-1615. doi: 10.1534/g3.117.039305. G3 (Bethesda). 2017. PMID: 28364038 Free PMC article.
-
The downstream box: an efficient and independent translation initiation signal in Escherichia coli.EMBO J. 1996 Feb 1;15(3):665-74. EMBO J. 1996. PMID: 8599950 Free PMC article.
-
The diversity of Shine-Dalgarno sequences sheds light on the evolution of translation initiation.RNA Biol. 2021 Nov;18(11):1489-1500. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2020.1861406. Epub 2020 Dec 21. RNA Biol. 2021. PMID: 33349119 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Translation initiation in Escherichia coli: old and new questions.Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jul;4(7):1063-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00679.x. Mol Microbiol. 1990. PMID: 1700254 Review.
Cited by
-
A standardized genome architecture for bacterial synthetic biology (SEGA).Nat Commun. 2021 Oct 7;12(1):5876. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-26155-5. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34620865 Free PMC article.
-
Growth resumption from stationary phase reveals memory in Escherichia coli cultures.Sci Rep. 2016 Apr 6;6:24055. doi: 10.1038/srep24055. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27048851 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of the spacer region between the Shine-Dalgarno box and the start codon for fine-tuning of the translation efficiency in Escherichia coli.Microb Biotechnol. 2020 Jul;13(4):1254-1261. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.13561. Epub 2020 Mar 23. Microb Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32202698 Free PMC article.
-
An extended Shine-Dalgarno sequence in mRNA functionally bypasses a vital defect in initiator tRNA.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Oct 7;111(40):E4224-33. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1411637111. Epub 2014 Sep 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 25246575 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidating the 16S rRNA 3' boundaries and defining optimal SD/aSD pairing in Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis using RNA-Seq data.Sci Rep. 2017 Dec 15;7(1):17639. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-17918-6. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29247194 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

