Uncertainty in heterogeneity estimates in meta-analyses
- PMID: 17974687
- PMCID: PMC2048840
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.39343.408449.80
Uncertainty in heterogeneity estimates in meta-analyses
Abstract
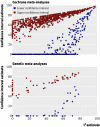
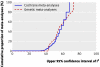
John Ioannidis, Nikolaos Patsopoulos, and Evangelos Evangelou argue that, although meta-analyses often measure heterogeneity between studies, these estimates can have large uncertainty, which must be taken into account when interpreting evidence
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Lau J, Ioannidis JPA, Schmid CH. Summing up evidence: one answer is not always enough. Lancet 1998;351:123-7. - PubMed
-
- Sutton A, Abrams K, Jones D, Sheldon T, Song F. Methods for meta-analysis in medical research Chichester: Wiley, 2000
-
- Petitti DB. Approaches to heterogeneity in meta-analysis. Stat Med 2001;20:3625-33. - PubMed
-
- Cochran WG. The combination of estimates from different experiments. Biometrics 1954;10:101-29.
-
- Higgins JPT, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med 2002;21:1539-58. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
