Förster transfer recovery reveals that phospholamban exchanges slowly from pentamers but rapidly from the SERCA regulatory complex
- PMID: 17975108
- PMCID: PMC2590498
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.107.159947
Förster transfer recovery reveals that phospholamban exchanges slowly from pentamers but rapidly from the SERCA regulatory complex
Abstract
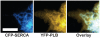
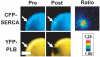
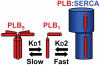
Phospholamban (PLB) or the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA) were fused to cyan fluorescent protein (CFP) and coexpressed with PLB fused to yellow fluorescent protein (YFP). The expressed fluorescently tagged proteins were imaged using epifluorescence and total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy. YFP fluorescence was selectively bleached by a focused laser beam. CFP fluorescence at the targeted site increased after YFP photobleaching, indicating fluorescence resonance energy transfer between CFP-SERCA/CFP-PLB and YFP-PLB. The increased donor fluorescence relaxed back toward baseline as a result of donor diffusion and exchange of bleached YFP-PLB for unbleached YFP-PLB, which restored fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Requenching of CFP donors, termed Förster transfer recovery (FTR), was quantified as an index of the rate of PLB subunit exchange from the PLB:SERCA and PLB:PLB membrane complexes. PLB subunit exchange from the PLB:SERCA regulatory complex was rapid, showing diffusion-limited FTR (tau=1.4 second). Conversely, PLB:PLB oligomeric complexes were found to be stable on a much longer time scale. Despite free lateral diffusion in the membrane, they showed no FTR over 80 seconds. Mutation of PLB position 40 from isoleucine to alanine (I40A-PLB) did not abolish PLB:PLB energy transfer, but destabilization of the PLB:PLB complex was apparent from an increased FTR rate (tau=8.4 seconds). Oligomers of I40A-PLB were stabilized by oxidative crosslinking of transmembrane cysteines with diamide. We conclude that PLB exchanges rapidly from its regulatory complex with the SERCA pump, whereas subunit exchange from the PLB oligomeric complex is slow and does not occur on the time scale of the cardiac cycle.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Phospholamban C-terminal residues are critical determinants of the structure and function of the calcium ATPase regulatory complex.J Biol Chem. 2014 Sep 12;289(37):25855-66. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.562579. Epub 2014 Jul 29. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25074938 Free PMC article.
-
Phospholamban oligomerization, quaternary structure, and sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum calcium ATPase binding measured by fluorescence resonance energy transfer in living cells.J Biol Chem. 2008 May 2;283(18):12202-11. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M707590200. Epub 2008 Feb 19. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18287099 Free PMC article.
-
Phospholamban mutants compete with wild type for SERCA binding in living cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012 Apr 6;420(2):236-40. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.02.125. Epub 2012 Mar 1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012. PMID: 22405774 Free PMC article.
-
Phospholamban and sarcolipin: Are they functionally redundant or distinct regulators of the Sarco(Endo)Plasmic Reticulum Calcium ATPase?J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2016 Feb;91:81-91. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2015.12.030. Epub 2015 Dec 29. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 26743715 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Direct spectroscopic detection of molecular dynamics and interactions of the calcium pump and phospholamban.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998 Sep 16;853:186-94. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1998.tb08266.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998. PMID: 10603946 Review.
Cited by
-
SERCA2a-phospholamban interaction monitored by an interposed circularly permutated green fluorescent protein.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2021 Jun 1;320(6):H2188-H2200. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00858.2020. Epub 2021 Apr 16. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33861144 Free PMC article.
-
Phospholamban C-terminal residues are critical determinants of the structure and function of the calcium ATPase regulatory complex.J Biol Chem. 2014 Sep 12;289(37):25855-66. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.562579. Epub 2014 Jul 29. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25074938 Free PMC article.
-
Dwarf open reading frame (DWORF) is a direct activator of the sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium pump SERCA.Elife. 2021 Jun 2;10:e65545. doi: 10.7554/eLife.65545. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34075877 Free PMC article.
-
Dysferlin forms a dimer mediated by the C2 domains and the transmembrane domain in vitro and in living cells.PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e27884. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027884. Epub 2011 Nov 14. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22110769 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of the Arg9Cys and Arg25Cys mutations on phospholamban's conformational equilibrium in membrane bilayers.Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2018 Jun;1860(6):1335-1341. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2018.02.030. Epub 2018 Mar 2. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2018. PMID: 29501609 Free PMC article.
References
-
- MacLennan DH, Kranias EG. Phospholamban: a crucial regulator of cardiac contractility. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003;4:566–577. - PubMed
-
- Asahi M, McKenna E, Kurzydlowski K, Tada M, MacLennan DH. Physical interactions between phospholamban and sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPases are dissociated by elevated Ca2+, but not by phospholamban phosphorylation, vanadate, or thapsigargin, and are enhanced by ATP. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:15034–15038. - PubMed
-
- Chen Z, Akin BL, Stokes DL, Jones LR. Cross-linking of C-terminal residues of phospholamban to the Ca2+ pump of cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum to probe spatial and functional interactions within the transmembrane domain. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:14163–14172. - PubMed
-
- Li J, Bigelow DJ, Squier TC. Conformational changes within the cytosolic portion of phospholamban upon release of Ca-ATPase inhibition. Biochemistry. 2004;43:3870–3879. - PubMed
-
- Mueller B, Karim CB, Negrashov IV, Kutchai H, Thomas DD. Direct detection of phospholamban and sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca-ATPase interaction in membranes using fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Biochemistry. 2004;43:8754–8765. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

