Gremlin-mediated decrease in bone morphogenetic protein signaling promotes pulmonary fibrosis
- PMID: 17975199
- PMCID: PMC2218851
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.200706-945OC
Gremlin-mediated decrease in bone morphogenetic protein signaling promotes pulmonary fibrosis
Abstract
Rationale: Members of the transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta superfamily, including TGF-betas and bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs), are essential for the maintenance of tissue homeostasis and regeneration after injury. We have observed that the BMP antagonist, gremlin, is highly up-regulated in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF).
Objectives: To investigate the role of gremlin in the regulation of BMP signaling in pulmonary fibrosis.
Methods: Progressive asbestos-induced fibrosis in the mouse was used as a model of human IPF. TGF-beta and BMP expression and signaling activities were measured from murine and human fibrotic lungs. The mechanism of gremlin induction was analyzed in cultured lung epithelial cells. In addition, the possible therapeutic role of gremlin inhibition was tested by administration of BMP-7 to mice after asbestos exposure.
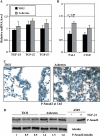
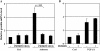
Measurements and main results: Gremlin mRNA levels were up-regulated in the asbestos-exposed mouse lungs, which is in agreement with the human IPF biopsy data. Down-regulation of BMP signaling was demonstrated by reduced levels of Smad1/5/8 and enhanced Smad2 phosphorylation in asbestos-treated lungs. Accordingly, analyses of cultured human bronchial epithelial cells indicated that asbestos-induced gremlin expression could be prevented by inhibitors of the TGF-beta receptor and also by inhibitors of the mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase/extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase pathways. BMP-7 treatment significantly reduced hydroxyproline contents in the asbestos-treated mice.
Conclusions: The TGF-beta and BMP signaling balance is important for lung regenerative events and is significantly perturbed in pulmonary fibrosis. Rescue of BMP signaling activity may represent a potential beneficial strategy for treating human pulmonary fibrosis.
Figures

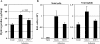
Similar articles
-
Bone morphogenetic protein-4 inhibitor gremlin is overexpressed in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Am J Pathol. 2006 Jul;169(1):61-71. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2006.051263. Am J Pathol. 2006. PMID: 16816361 Free PMC article.
-
Gremlin is a key pro-fibrogenic factor in chronic pancreatitis.J Mol Med (Berl). 2015 Oct;93(10):1085-1093. doi: 10.1007/s00109-015-1308-9. Epub 2015 Jul 5. J Mol Med (Berl). 2015. PMID: 26141517 Free PMC article.
-
Bone morphogenetic protein 7 suppresses the progression of hepatic fibrosis and regulates the expression of gremlin and transforming growth factor β1.Mol Med Rep. 2012 Jul;6(1):246-52. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2012.892. Epub 2012 Apr 26. Mol Med Rep. 2012. PMID: 22552821
-
Bone morphogenetic proteins.Growth Factors. 2004 Dec;22(4):233-41. doi: 10.1080/08977190412331279890. Growth Factors. 2004. PMID: 15621726 Review.
-
Emerging role of BMPs/BMPR2 signaling pathway in treatment for pulmonary fibrosis.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Sep;178:117178. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.117178. Epub 2024 Aug 13. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 39142248 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gremlin-1 Overexpression in Mouse Lung Reduces Silica-Induced Lymphocyte Recruitment - A Link to Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis through Negative Correlation with CXCL10 Chemokine.PLoS One. 2016 Jul 18;11(7):e0159010. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0159010. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27428020 Free PMC article.
-
High-throughput screens for agonists of bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling identify potent benzoxazole compounds.J Biol Chem. 2019 Mar 1;294(9):3125-3136. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.006817. Epub 2019 Jan 2. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30602563 Free PMC article.
-
GREM1/PPP2R3A expression in heterogeneous fibroblasts initiates pulmonary fibrosis.Cell Biosci. 2022 Aug 6;12(1):123. doi: 10.1186/s13578-022-00860-0. Cell Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35933397 Free PMC article.
-
Opposing Roles of BMP and TGF-β Signaling Pathways in Pancreatitis: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implication.Adv Res Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;13(5):555871. Epub 2019 Sep 4. Adv Res Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 32211568 Free PMC article.
-
Gremlin activates the Smad pathway linked to epithelial mesenchymal transdifferentiation in cultured tubular epithelial cells.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:802841. doi: 10.1155/2014/802841. Epub 2014 May 18. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 24949470 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kingsley D. The TGF-β superfamily: new members, new receptors, and new genetic tests of function in different organisms. Genes Dev 1994;8:133–146. - PubMed
-
- Bierie B, Moses HL. Tumour microenvironment: TGF-β: the molecular Jekyll and Hyde of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2006;6:506–520. - PubMed
-
- Branton MH, Kopp JB. TGF-β and fibrosis. Microbes Infect 1999;1:1349–1365. - PubMed
-
- Bartram U, Speer CP. The role of transforming growth factor-β in lung development and disease. Chest 2004;125:754–765. - PubMed
-
- Bellusci S, Henderson R, Winnier G, Oikawa T, Hogan BL. Evidence from normal expression and targeted misexpression that bone morphogenetic protein (Bmp-4) plays a role in mouse embryonic lung morphogenesis. Development 1996;122:1693–1702. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

