Kidney kinase network regulates renal ion cotransport
- PMID: 17975663
- PMCID: PMC2045623
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI33859
Kidney kinase network regulates renal ion cotransport
Abstract
Protein kinases catalyze the phosphorylation of serine/threonine or tyrosine residues, which may directly alter a protein's functional properties. Kinases can also regulate protein functions indirectly, for example, by controlling the composition and/or subcellular localization of members of multiprotein complexes that associate with the regulated protein. In this issue of the JCI, two separate studies by Weinman et al. and Yang et al. examine the second of these two modes of kinase-mediated regulation and demonstrate the effects of kinases on two Na(+)-driven renal cotransporters (see the related articles beginning on pages 3403 and 3412). Their results reveal important implications for phosphate and salt homeostasis, respectively.
Figures
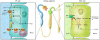
Comment on
-
The thiazide-sensitive Na-Cl cotransporter is regulated by a WNK kinase signaling complex.J Clin Invest. 2007 Nov;117(11):3403-11. doi: 10.1172/JCI32033. J Clin Invest. 2007. PMID: 17975670 Free PMC article.
-
Parathyroid hormone inhibits renal phosphate transport by phosphorylation of serine 77 of sodium-hydrogen exchanger regulatory factor-1.J Clin Invest. 2007 Nov;117(11):3412-20. doi: 10.1172/JCI32738. J Clin Invest. 2007. Retraction in: J Clin Invest. 2013 Jun;123(6):2752. doi: 10.1172/JCI70657. PMID: 17975671 Free PMC article. Retracted.
Similar articles
-
Protein kinase C activators induce membrane retrieval of type II Na+-phosphate cotransporters expressed in Xenopus oocytes.J Physiol. 1999 Jun 1;517 ( Pt 2)(Pt 2):327-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.0327t.x. J Physiol. 1999. PMID: 10332085 Free PMC article.
-
Forging the link between structure and function of electrogenic cotransporters: the renal type IIa Na+/Pi cotransporter as a case study.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2002 Nov;80(3):69-108. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6107(02)00015-9. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2002. PMID: 12379267 Review.
-
[Discovery of alpha-Klotho and FGF23 unveiled new insight into calcium and phosphate homeostasis].Clin Calcium. 2008 Jul;18(7):923-34. Clin Calcium. 2008. PMID: 18591743 Review. Japanese.
-
Regulation of Renal Electrolyte Transport by WNK and SPAK-OSR1 Kinases.Annu Rev Physiol. 2016;78:367-89. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-021115-105431. Annu Rev Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26863326 Review.
-
Sodium-hydrogen exchanger regulatory factor 1 (NHERF-1) transduces signals that mediate dopamine inhibition of sodium-phosphate co-transport in mouse kidney.J Biol Chem. 2010 Apr 30;285(18):13454-60. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.094359. Epub 2010 Mar 3. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20200151 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Oncogenic osteomalacia caused by a phosphaturic mesenchymal tumor of the femur: A case report.World J Clin Cases. 2019 Aug 6;7(15):2081-2086. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i15.2081. World J Clin Cases. 2019. PMID: 31423441 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Murer H., Forster I., Biber J. The sodium phosphate cotransporter family SLC34. Pflugers Arch. 2004;447:763–767. - PubMed
-
- Hebert S.C., Mount D.B., Gamba G. Molecular physiology of cation-coupled Cl-cotransport: the SLC12 family. Pflugers Arch. 2004;447:580–593. - PubMed
-
- Gamba G. Molecular physiology and pathophysiology of electroneutral cation-chloride cotransporters. Physiol. Rev. 2005;85:423–493. - PubMed

