Identification of HLA-DR-bound peptides presented by human bronchoalveolar lavage cells in sarcoidosis
- PMID: 17975675
- PMCID: PMC2045606
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI32401
Identification of HLA-DR-bound peptides presented by human bronchoalveolar lavage cells in sarcoidosis
Abstract
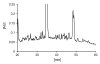
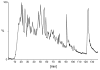
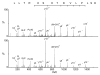
Sarcoidosis is an inflammatory disease of unknown etiology, most commonly affecting the lungs. Activated CD4+ T cells accumulate in the lungs of individuals with sarcoidosis and are considered to be of central importance for inflammation. We have previously shown that Scandinavian sarcoidosis patients expressing the HLA-DR allele DRB1*0301 are characterized by large accumulations in the lungs of CD4+ T cells expressing the TCR AV2S3 gene segment. This association afforded us a unique opportunity to identify a sarcoidosis-specific antigen recognized by AV2S3+ T cells. To identify candidates for the postulated sarcoidosis-specific antigen, lung cells from 16 HLA-DRB1*0301pos patients were obtained by bronchoalveolar lavage. HLA-DR molecules were affinity purified and bound peptides acid eluted. Subsequently, peptides were separated by reversed-phase HPLC and analyzed by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. We identified 78 amino acid sequences from self proteins presented in the lungs of sarcoidosis patients, some of which were well-known autoantigens such as vimentin and ATP synthase. For the first time, to our knowledge, we have identified HLA-bound peptides presented in vivo during an inflammatory condition. This approach can be extended to characterize HLA-bound peptides in various autoimmune settings.
Figures
Comment in
-
The saga of MHC-bound peptides: a renaissance for antigen presentation?J Clin Invest. 2007 Nov;117(11):3164-6. doi: 10.1172/JCI33997. J Clin Invest. 2007. PMID: 17975658 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Lung restricted T cell receptor AV2S3+ CD4+ T cell expansions in sarcoidosis patients with a shared HLA-DRbeta chain conformation.Thorax. 2002 Apr;57(4):348-52. doi: 10.1136/thorax.57.4.348. Thorax. 2002. PMID: 11923555 Free PMC article.
-
Autoimmune T cell responses to antigenic peptides presented by bronchoalveolar lavage cell HLA-DR molecules in sarcoidosis.Clin Immunol. 2009 Dec;133(3):353-63. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2009.08.008. Epub 2009 Sep 27. Clin Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19786367
-
T-cell receptor-HLA-DRB1 associations suggest specific antigens in pulmonary sarcoidosis.Eur Respir J. 2016 Mar;47(3):898-909. doi: 10.1183/13993003.01209-2015. Epub 2015 Nov 19. Eur Respir J. 2016. PMID: 26585430
-
[Studies of T-lymphocytes in pursuit of sarcoidosis antigens].Lakartidningen. 2002 Sep 5;99(36):3508-13, 3515. Lakartidningen. 2002. PMID: 12362750 Review. Swedish.
-
Role of CD4+ T cells in sarcoidosis.Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2007 Aug 15;4(5):461-4. doi: 10.1513/pats.200606-130MS. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2007. PMID: 17684290 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Cutibacterium acnes in Sarcoidosis: From Antigen to Treatable Trait?Microorganisms. 2022 Aug 15;10(8):1649. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10081649. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36014067 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Meta-analysis of genetic programs between idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and sarcoidosis.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 14;8(8):e71059. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071059. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23967151 Free PMC article.
-
Classical Examples of the Concept of the ASIA Syndrome.Biomolecules. 2020 Oct 12;10(10):1436. doi: 10.3390/biom10101436. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 33053910 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of HLA ligand elution data and binding predictions reveals varying prediction performance for the multiple motifs recognized by HLA-DQ2.5.Immunology. 2021 Feb;162(2):235-247. doi: 10.1111/imm.13279. Epub 2020 Nov 3. Immunology. 2021. PMID: 33064841 Free PMC article.
-
Mass spectrometry-assisted identification of ADAMTS13-derived peptides presented on HLA-DR and HLA-DQ.Haematologica. 2018 Jun;103(6):1083-1092. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2017.179119. Epub 2018 Mar 22. Haematologica. 2018. PMID: 29567779 Free PMC article.
References
-
- [No authors listed]. . Statement on sarcoidosis. Joint Statement of the American Thoracic Society (ATS), the European Respiratory Society (ERS) and the World Association of Sarcoidosis and Other Granulomatous Disorders (WASOG) adopted by the ATS Board of Directors and by the ERS Executive Committee, February 1999. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999;160:736–755. - PubMed
-
- Newman L.S., Rose C.S., Maier L.A. Sarcoidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997;336:1224–1234. - PubMed
-
- Planck A., Eklund A., Grunewald J. Markers of activity in clinically recovered human leukocyte antigen- DR17-positive sarcoidosis patients. Eur. Respir. J. 2003;21:52–57. - PubMed
-
- Grunewald J., Berlin M., Olerup O., Eklund A. Lung T-helper cells expressing T-cell receptor AV2S3 associate with clinical features of pulmonary sarcoidosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000;161:814–818. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

