Polycystic kidney diseases: from molecular discoveries to targeted therapeutic strategies
- PMID: 17975706
- PMCID: PMC2775119
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-007-7362-x
Polycystic kidney diseases: from molecular discoveries to targeted therapeutic strategies
Abstract
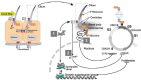
Polycystic kidney diseases (PKDs) represent a large group of progressive renal disorders characterized by the development of renal cysts leading to end-stage renal disease. Enormous strides have been made in understanding the pathogenesis of PKDs and the development of new therapies. Studies of autosomal dominant and recessive polycystic kidney diseases converge on molecular mechanisms of cystogenesis, including ciliary abnormalities and intracellular calcium dysregulation, ultimately leading to increased proliferation, apoptosis and dedifferentiation. Here we review the pathobiology of PKD, highlighting recent progress in elucidating common molecular pathways of cystogenesis. We discuss available models and challenges for therapeutic discovery as well as summarize the results from preclinical experimental treatments targeting key disease-specific pathways.
Figures



Similar articles
-
mTOR signaling in polycystic kidney disease.Trends Mol Med. 2011 Nov;17(11):625-33. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2011.06.003. Epub 2011 Jul 19. Trends Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 21775207 Review.
-
[Recent advances in molecular pathogenesis and treatment of polycystic kidney disease].Rev Med Chir Soc Med Nat Iasi. 2008 Jan-Mar;112(1):11-20. Rev Med Chir Soc Med Nat Iasi. 2008. PMID: 18677899 Review. Romanian.
-
Recent advances in the understanding of polycystic kidney disease.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 1997 Jul;6(4):377-83. doi: 10.1097/00041552-199707000-00012. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 1997. PMID: 9263688 Review.
-
Regulation of ciliary trafficking of polycystin-2 and the pathogenesis of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2010 Feb;35(2):93-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7347.2010.02.001. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2010. PMID: 20197605 Review.
-
The molecular biology of polycystic kidney disease.Pediatr Nephrol. 1998 Nov;12(9):721-6. doi: 10.1007/s004670050534. Pediatr Nephrol. 1998. PMID: 9874315 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of PKR in the Inhibition of Proliferation and Translation by Polycystin-1.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Jun 23;2019:5320747. doi: 10.1155/2019/5320747. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31341901 Free PMC article.
-
The primary cilium as a cellular signaling center: lessons from disease.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2009 Jun;19(3):220-9. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2009.04.008. Epub 2009 May 22. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2009. PMID: 19477114 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Congenital hepatic fibrosis in autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease.Clin Transl Sci. 2011 Dec;4(6):460-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1752-8062.2011.00306.x. Epub 2011 Dec 7. Clin Transl Sci. 2011. PMID: 22212229 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ouabain Enhances ADPKD Cell Apoptosis via the Intrinsic Pathway.Front Physiol. 2016 Mar 24;7:107. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2016.00107. eCollection 2016. Front Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27047392 Free PMC article.
-
microRNA biomarkers in cystic diseases.BMB Rep. 2013 Jul;46(7):338-45. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2013.46.7.151. BMB Rep. 2013. PMID: 23884099 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Friedman J. Cystic diseases of the kidney. In: Emery A., Rimoin D., editors. Principles and practice of medical genetics. Edinburgh, UK: Churchill Livingston; 1983. pp. 1002–1010.
-
- Parfrey P. S., Bear J. C., Morgan J., Cramer B. C., McManamon P. J., Gault M. H., Churchill D. N., Singh M., Hewitt R., Somlo S., Reeders S. The diagnosis and prognosis of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990;323:1085–1090. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199010183231601. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

