Determinants of protein function revealed by combinatorial entropy optimization
- PMID: 17976239
- PMCID: PMC2258190
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2007-8-11-r232
Determinants of protein function revealed by combinatorial entropy optimization
Abstract
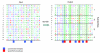
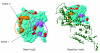
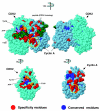
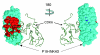
We use a new algorithm (combinatorial entropy optimization [CEO]) to identify specificity residues and functional subfamilies in sets of proteins related by evolution. Specificity residues are conserved within a subfamily but differ between subfamilies, and they typically encode functional diversity. We obtain good agreement between predicted specificity residues and experimentally known functional residues in protein interfaces. Such predicted functional determinants are useful for interpreting the functional consequences of mutations in natural evolution and disease.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Septins: a highly conserved family of membrane-associated GTPases with functions in cell division and beyond.J Membr Biol. 1999 May 15;169(2):75-81. doi: 10.1007/s002329900519. J Membr Biol. 1999. PMID: 10341029 Review. No abstract available.
-
Cellular functions of TC10, a Rho family GTPase: regulation of morphology, signal transduction and cell growth.Oncogene. 1999 Jul 1;18(26):3831-45. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1202758. Oncogene. 1999. PMID: 10445846
-
Analysis of septins across kingdoms reveals orthology and new motifs.BMC Evol Biol. 2007 Jul 1;7:103. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-7-103. BMC Evol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17601340 Free PMC article.
-
Septins: a ring to part mother and daughter.Curr Genet. 2002 Jun;41(3):123-31. doi: 10.1007/s00294-002-0304-0. Epub 2002 Jun 19. Curr Genet. 2002. PMID: 12111093 Review.
-
GTPases: a family of molecular switches and clocks.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1995 Sep 29;349(1329):283-9. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1995.0114. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1995. PMID: 8577839 Review.
Cited by
-
MUFFINN: cancer gene discovery via network analysis of somatic mutation data.Genome Biol. 2016 Jun 23;17(1):129. doi: 10.1186/s13059-016-0989-x. Genome Biol. 2016. PMID: 27333808 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of computational methods for predicting the effects of missense mutations in human cancers.BMC Genomics. 2013;14 Suppl 3(Suppl 3):S7. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-S3-S7. Epub 2013 May 28. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23819521 Free PMC article.
-
Partially-supervised protein subclass discovery with simultaneous annotation of functional residues.BMC Struct Biol. 2009 Oct 26;9:68. doi: 10.1186/1472-6807-9-68. BMC Struct Biol. 2009. PMID: 19857261 Free PMC article.
-
Revisiting Two Decades of Research Focused on Targeting APE1 for Cancer Therapy: The Pros and Cons.Cells. 2023 Jul 20;12(14):1895. doi: 10.3390/cells12141895. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37508559 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discovery of oncogenic ROS1 missense mutations with sensitivity to tyrosine kinase inhibitors.EMBO Mol Med. 2023 Oct 11;15(10):e17367. doi: 10.15252/emmm.202217367. Epub 2023 Aug 17. EMBO Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37587872 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Greenblatt MS, Beaudet JG, Gump JR, Godin KS, Trombley L, Koh J, Bond JP. Detailed computational study of p53 and p16: using evolutionary sequence analysis and disease-associated mutations to predict the functional consequences of allelic variants. Oncogene. 2003;22:1150–1163. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206101. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

