Model membrane systems and their applications
- PMID: 17976391
- PMCID: PMC2196400
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2007.09.020
Model membrane systems and their applications
Abstract
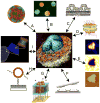
The complexity of biological membranes has motivated the development of a wide variety of simpler model systems whose size, geometry, and composition can be tailored with great precision. Approaches highlighted in this review are illustrated in Figure 1 including vesicles, supported bilayers, and hybrid membrane systems. These have been used to study problems ranging from phase behavior to membrane fusion. Experimental membrane models continue to advance in complexity with respect to architecture, size, and composition, as do computer simulations of their properties and dynamics. Analytical techniques such as imaging secondary ion mass spectrometry have also been developed and refined to give increasing spatial resolution and information content on membrane composition and dynamics.
Figures
References
-
- Baumgart T, Hunt G, Farkas ER, Webb WW, Feigenson GW. Fluorescence probe partitioning between Lo/Ld phases in lipid membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007 doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2007.05.012. The partitioning behavior of 26 fluorophores into lo and ld phases in GUV’s is reported. Most lipid-conjugated fluorophores partition into the ld phase, while DiI derivatives and polyaromatic hydrocarbons showed more mixed behavior. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baumgart T, Hammond AT, Sengupta P, Hess ST, Holowka DA, Baird BA, Webb WW. Large-scale fluid/fluid phase separation of proteins and lipids in giant plasma membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:3165–3170. Giant plasma membrane vesicles derived from mammalian cells are shown to exhibit phase separation at sub-physiological temperatures. The phase partitioning behavior of fluorescent lipids and labeled proteins are also described. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

