Regulated expression of microRNAs in normal and polycythemia vera erythropoiesis
- PMID: 17976518
- PMCID: PMC2699372
- DOI: 10.1016/j.exphem.2007.08.021
Regulated expression of microRNAs in normal and polycythemia vera erythropoiesis
Abstract
Objective: Polycythemia vera (PV) is a myeloproliferative disorder, arising from the acquired mutation(s) of a hematopoietic stem cell. The JAK2 V617F somatic mutation is found in most PV patients; however, it is not the disease-initiating mutation. Because microRNAs (miRNAs) play a regulatory role in hematopoiesis, we studied miRNA expressions in PV and normal erythropoiesis.
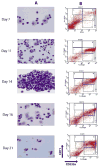
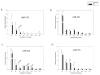
Methods: Peripheral blood mononuclear cells were cultured in a three-phase liquid system resulting in synchronized expansion of erythroid progenitors. Using gene-expression profiling by CombiMatrix MicroRNArray, we searched for PV-specific changes at days 1, 14, and 21. Twelve miRNA candidates were then reevaluated by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction in a larger number of samples obtained from progenitors at the same stage of differentiation.
Results: A significant difference in miR-150 expression was found in PV. In normal erythropoiesis, three expression patterns of miRNAs were observed: progressive downregulation of miR-150, miR-155, miR-221, miR-222; upregulation of miR-451, miR-16 at late stages of erythropoiesis; and biphasic regulation of miR-339, miR-378. The miR-451 appears to be erythroid-specific.
Conclusions: We identified the miRNAs with regulated expression in erythropoiesis; one appeared to be PV-specific. Their miRNA expression levels define early, intermediate, and late stages of erythroid differentiation. The validity of our findings was confirmed in nonexpanded peripheral blood cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures

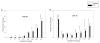
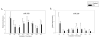

References
-
- Bellucci S, Michiels JJ. The role of JAK2 V617F mutation, spontaneous erythropoiesis and megakaryocytopoiesis, hypersensitive platelets, activated leukocytes, and endothelial cells in the etiology of thrombotic manifestations in polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2006;32:381–398. - PubMed
-
- Levine RL, Gilliland DG. JAK-2 mutations and their relevance to myeloproliferative disease. Curr Opin Hematol. 2007;14:43–47. - PubMed
-
- Rumi E, Passamonti F, Pietra D, et al. JAK2 (V617F) as an acquired somatic mutation and a secondary genetic event associated with disease progression in familial myeloproliferative disorders. Cancer. 2006;107:2206–2211. - PubMed
-
- Lippert E, Boissinot M, Kralovics R, et al. The JAK2-V617F mutation is frequently present at diagnosis in patients with essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera. Blood. 2006;108:1865–1867. - PubMed
-
- Nussenzveig RH, Swierczek SI, Jelinek J, et al. Polycythemia vera is not initiated by JAK2V617F mutation. Exp Hematol. 2007;35:32–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

