unc-94 encodes a tropomodulin in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 17976644
- PMCID: PMC2175264
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.10.005
unc-94 encodes a tropomodulin in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
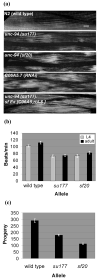
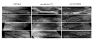
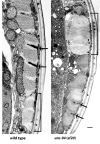
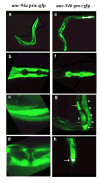
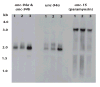
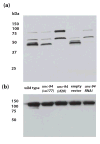
unc-94 is one of about 40 genes in Caenorhabditis elegans that, when mutant, displays an abnormal muscle phenotype. Two mutant alleles of unc-94, su177 and sf20, show reduced motility and brood size and disorganization of muscle structure. In unc-94 mutants, immunofluorescence microscopy shows that a number of known sarcomeric proteins are abnormal, but the most dramatic effect is in the localization of F-actin, with some abnormally accumulated near muscle cell-to-cell boundaries. Electron microscopy shows that unc-94(sf20) mutants have large accumulations of thin filaments near the boundaries of adjacent muscle cells. Multiple lines of evidence prove that unc-94 encodes a tropomodulin, a conserved protein known from other systems to bind to both actin and tropomyosin at the pointed ends of actin thin filaments. su177 is a splice site mutation in intron 1, which is specific to one of the two unc-94 isoforms, isoform a; sf20 has a stop codon in exon 5, which is shared by both isoform a and isoform b. The use of promoter-green fluorescent protein constructs in transgenic animals revealed that unc-94a is expressed in body wall, vulval and uterine muscles, whereas unc-94b is expressed in pharyngeal, anal depressor, vulval and uterine muscles and in spermatheca and intestinal epithelial cells. By Western blot, anti-UNC-94 antibodies detect polypeptides of expected size from wild type, wild-type-sized proteins of reduced abundance from unc-94(su177), and no detectable unc-94 products from unc-94(sf20). Using these same antibodies, UNC-94 localizes as two closely spaced parallel lines flanking the M-lines, consistent with localization to the pointed ends of thin filaments. In addition, UNC-94 is localized near muscle cell-to-cell boundaries.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Actin filament disassembling activity of Caenorhabditis elegans actin-interacting protein 1 (UNC-78) is dependent on filament binding by a specific ADF/cofilin isoform.J Cell Sci. 2003 Oct 15;116(Pt 20):4107-18. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00717. Epub 2003 Sep 2. J Cell Sci. 2003. PMID: 12953066
-
The minus-end actin capping protein, UNC-94/tropomodulin, regulates development of the Caenorhabditis elegans intestine.Dev Dyn. 2014 Jun;243(6):753-64. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.24118. Epub 2014 Mar 12. Dev Dyn. 2014. PMID: 24677443 Free PMC article.
-
Sarcomeric actin organization is synergistically promoted by tropomodulin, ADF/cofilin, AIP1 and profilin in C. elegans.J Cell Sci. 2008 Dec 1;121(Pt 23):3867-77. doi: 10.1242/jcs.040477. Epub 2008 Nov 4. J Cell Sci. 2008. PMID: 18984629 Free PMC article.
-
Tropomodulin capping of actin filaments in striated muscle development and physiology.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011;2011:103069. doi: 10.1155/2011/103069. Epub 2011 Oct 17. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 22013379 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Capping actin filament growth: tropomodulin in muscle and nonmuscle cells.Soc Gen Physiol Ser. 1997;52:79-89. Soc Gen Physiol Ser. 1997. PMID: 9210222 Review.
Cited by
-
Tropomodulins: pointed-end capping proteins that regulate actin filament architecture in diverse cell types.Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2012 Jun;69(6):337-70. doi: 10.1002/cm.21031. Epub 2012 May 4. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2012. PMID: 22488942 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multifunctional roles of tropomodulin-3 in regulating actin dynamics.Biophys Rev. 2018 Dec;10(6):1605-1615. doi: 10.1007/s12551-018-0481-9. Epub 2018 Nov 14. Biophys Rev. 2018. PMID: 30430457 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DAAM is required for thin filament formation and Sarcomerogenesis during muscle development in Drosophila.PLoS Genet. 2014 Feb 27;10(2):e1004166. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004166. eCollection 2014 Feb. PLoS Genet. 2014. PMID: 24586196 Free PMC article.
-
Actin-ADF/cofilin rod formation in Caenorhabditis elegans muscle requires a putative F-actin binding site of ADF/cofilin at the C-terminus.Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2009 Jul;66(7):398-408. doi: 10.1002/cm.20383. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2009. PMID: 19459188 Free PMC article.
-
Levamisole and ryanodine receptors. I: A contraction study in Ascaris suum.Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2010 May;171(1):1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2009.12.007. Epub 2010 Jan 11. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2010. PMID: 20064566 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Waterston RH. Muscle. In: Wood WB, editor. The Nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; Cold Spring Harbor, New York: 1988. pp. 281–335.
-
- Moerman DG, Fire A. Muscle: structure, function and development. In: Riddle DL, Blumenthal T, Meyer BJ, Priess JR, editors. C elegans II. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; Cold Spring Harbor, New York: 1997. pp. 417–470. - PubMed
-
- Moerman DG, Williams BD. Sarcomere assembly in C. elegans muscle. Wormbook, ed. The C. elegans Research Community, WormBook. Jan 16, 2006. http://www.wormbook.org. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

