Fast oscillations associated with interictal spikes localize the epileptogenic zone in patients with partial epilepsy
- PMID: 17977022
- PMCID: PMC2742724
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.09.036
Fast oscillations associated with interictal spikes localize the epileptogenic zone in patients with partial epilepsy
Abstract
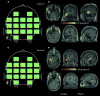
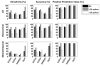
Although interictal epileptic spikes are defined as fast transient activity, the spatial distribution of spike-related high-frequency power changes is unknown. In this study, we localized the sources of spike-locked power increases in the beta and gamma band with magnetoencephalography and an adaptive spatial filtering technique and tested the usefulness of these reconstructions for determining the epileptogenic zone in a population of 27 consecutive presurgical patients with medication refractory partial epilepsies. The reliability of this approach was compared to the performance of conventional MEG techniques such as equivalent current dipole (ECD) models. In patients with good surgical outcome after a mean follow-up time of 16 months (Engel class I or II), the surgically resected area was identified with an accuracy of 85% by sources of spike-locked beta/gamma activity, which compared favorably with the accuracy of 69% found for ECD models of single spikes. In patients with a total of more than 50 spikes in their recordings, the accuracies increased to 100% vs. 88%, respectively. Imaging of spike-locked beta/gamma power changes therefore seems to be a reliable and fast alternative to conventional MEG techniques for localizing epileptogenic tissue, in particular, if more than 50 interictal spikes can be recorded.
Figures
References
-
- Engel J, Jr, Rasmussen TB. Surgical Treatment of the Epilepsies. 2. Raven Press; New York: 1993. Outcome with respect to epileptic seizures; pp. 609–621.
-
- IFSECN. A glossary of terms most commonly used by clinical electroencephalographers. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1974;37:538–548. - PubMed
-
- Kirsch HE, Robinson SE, Mantle M, Nagarajan S. Automated localization of magnetoencephalographic interictal spikes by adaptive spatial filtering. Clin Neurophysiol. 2006;117:2264–2271. - PubMed
-
- Knowlton RC, Elgavish R, Howell J, Blount J, Burneo JG, Faught E, Kankirawatana P, Riley K, Morawetz R, Worthington J, Kuzniecky RI. Magnetic source imaging versus intracranial electroencephalogram in epilepsy surgery: a prospective study. Ann Neurol. 2006;59:835–842. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

