Bioavailability of apocynin through its conversion to glycoconjugate but not to diapocynin
- PMID: 17977702
- PMCID: PMC2527211
- DOI: 10.1016/j.phymed.2007.09.019
Bioavailability of apocynin through its conversion to glycoconjugate but not to diapocynin
Abstract
Apocynin (4-hydroxy-3-methoxyacetophenone) is a major active ingredient from the rhizomes of Picrorhiza kurroa, a botanical plant used as an herbal medicine for treatment of a number of inflammatory diseases. Recently, apocynin is regarded as a specific inhibitor for NADPH oxidase in cell and animal models. In vitro studies indicated conversion of apocynin to diapocynin in the presence of peroxidases, e.g., myloperoxidase, posing the possibility that diapocynin also contributes to the anti-oxidative action of apocynin. The objectives of this study are to examine the bioavailability of apocynin to plasma, liver and brain tissue after intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection, and to examine whether apocynin is converted to diapocynin in vivo. Diapocynin was chemically synthetized and characterized by NMR and IR. Apocynin (5mg/kg body wt) was injected i.p. to adult male Sprague-Dawley rats and plasma, liver and brain were collected at different times (30min, 1 and 2h) after injection. Samples were treated with beta-glucuronidase to hydrolyze the glycosyl linkage and analyzed by HPLC/MS. At 30min and 1h after injection, approximately 50% of apocynin was converted to its glycosyl derivative and was distributed in plasma, liver and brain. No diapocynin was detected in any samples. These results indicate rapid glycosylation of apocynin and its transport to blood and other organs but no apparent conversion to diapocynin in vivo.
Figures


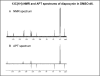


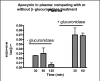

References
-
- Barbieri SS, Cavalca V, Eligini S, Brambilla M, Caiani A, Tremoli E, Colli S. Apocynin prevents cyclooxygenase 2 expression in human monocytes through NADPH oxidase and glutathione redox-dependent mechanisms. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2004;37:156–165. - PubMed
-
- Bedard K, Krause KH. The NOX family of ROS-generating NADPH oxidases: physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol. Rev. 2007;87:245–313. - PubMed
-
- Chan PH. Reactive oxygen radicals in signaling and damage in the ischemic brain. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2001;21:2–14. - PubMed
-
- Cotter MA, Cameron NE. Effect of the NAD(P)H oxidase inhibitor, apocynin, on peripheral nerve perfusion and function in diabetic rats. Life Sci. 2003;73:1813–1824. - PubMed
-
- Dasari M, Richards KM, Alt MA, Crawford CFP, Schleiden A, Ingram J, Aziz A, Hamidou AAA, Williams A, Chernovitz PA, Luo R, Sun GY, Luchtefeld R, Smith RE. Diapocynin Synthesis. J. Chem. Ed. 2008 in press.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

