TGFbeta1 and Treg cells: alliance for tolerance
- PMID: 17977791
- PMCID: PMC2805009
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molmed.2007.08.005
TGFbeta1 and Treg cells: alliance for tolerance
Abstract
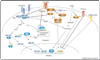
Transforming growth factor beta1 (TGFbeta1), an important pleiotropic, immunoregulatory cytokine, uses distinct signaling mechanisms in lymphocytes to affect T-cell homeostasis, regulatory T (Treg)-cell and effector-cell function and tumorigenesis. Defects in TGFbeta1 expression or its signaling in T cells correlate with the onset of several autoimmune diseases. TGFbeta1 prevents abnormal T-cell activation through the modulation of Ca2+-calcineurin signaling in a Caenorhabditis elegans Sma and Drosophila Mad proteins (SMAD)3 and SMAD4-independent manner; however, in Treg cells, its effects are mediated, at least in part, through SMAD signaling. TGFbeta1 also acts as a pro-inflammatory cytokine and induces interleukin (IL)-17-producing pathogenic T-helper cells (Th IL-17 cells) synergistically during an inflammatory response in which IL-6 is produced. Here, we will review TGFbeta1 and its signaling in T cells with an emphasis on the regulatory arm of immune tolerance.
Figures

References
-
- Miyara M, Sakaguchi S. Natural regulatory T cells: mechanisms of suppression. Trends Mol. Med. 2007;13:108–116. - PubMed
-
- Tang Q, et al. Distinct roles of CTLA-4 and TGFβ in CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cell function. Eur. J. Immunol. 2004;34:2996–3005. - PubMed
-
- Shevach EM. Regulatory/suppressor T cells in health and disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50:2721–2724. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

