Paramyxovirus-induced shutoff of host and viral protein synthesis: role of the P and V proteins in limiting PKR activation
- PMID: 17977969
- PMCID: PMC2224604
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02023-07
Paramyxovirus-induced shutoff of host and viral protein synthesis: role of the P and V proteins in limiting PKR activation
Abstract
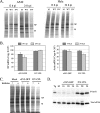
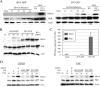
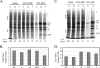
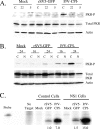
The paramyxovirus simian virus 5 (SV5) establishes highly productive persistent infections of epithelial cells without inducing a global inhibition of translation. Here we show that an SV5 mutant (the P/V-CPI(-) mutant) with substitutions in the P subunit of the viral polymerase and the accessory V protein also establishes highly productive infections like wild-type (WT) SV5 but that cells infected with the P/V-CPI(-) mutant show an overall shutdown of both host and viral translation at late times postinfection. Reduced host and viral protein synthesis with the P/V-CPI(-) virus was not due to lower levels of mRNA or caspase-dependent apoptosis and correlated with phosphorylation of the translation initiation factor eIF-2alpha. WT SV5 was a poor activator of the eIF-2alpha kinase protein kinase R (PKR). By contrast, the P/V-CPI(-) mutant induced PKR phosphorylation, which correlated with the time course of translation inhibition but was independent of interferon signaling. In HeLa cells that expressed the PKR inhibitor influenza A virus NS1 or reovirus sigma3, the rate of host protein synthesis at late times after infection with the P/V-CPI(-) mutant was restored to approximately 50% that of control HeLa cells. By contrast, the rates of P/V-CPI(-) viral protein synthesis in HeLa cells expressing NS1 or sigma3 were dramatically enhanced, between 5- and 20-fold, while levels of viral mRNA were increased only slightly (NS1-expressing cells) or remained constant (sigma3-expressing cells). Similar results were found using HeLa cells where PKR levels were reduced due to knockdown by small interfering RNA. Expression of either the WT P or the WT V protein from the genome of the P/V-CPI(-) mutant resulted in lower levels of PKR activation and rates of host and viral protein synthesis that closely matched those seen with WT SV5. Despite higher rates of translation, cells infected with the V- or P-complemented virus accumulated viral mRNAs to lower levels than that seen with the parental P/V-CPI(-) mutant. We present a model in which the paramyxovirus P/V gene products limit induction of PKR by limiting the synthesis of aberrant viral mRNAs and double-stranded RNA and thus prevent the shutdown of translation by a mechanism that differs from that of other PKR inhibitors such as NS1 and sigma3.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Naturally occurring substitutions in the P/V gene convert the noncytopathic paramyxovirus simian virus 5 into a virus that induces alpha/beta interferon synthesis and cell death.J Virol. 2002 Oct;76(20):10109-21. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.20.10109-10121.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 12239285 Free PMC article.
-
A simian virus 5 (SV5) P/V mutant is less cytopathic than wild-type SV5 in human dendritic cells and is a more effective activator of dendritic cell maturation and function.J Virol. 2006 Apr;80(7):3416-27. doi: 10.1128/JVI.80.7.3416-3427.2006. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16537609 Free PMC article.
-
Virus growth and antibody responses following respiratory tract infection of ferrets and mice with WT and P/V mutants of the paramyxovirus Simian Virus 5.Virology. 2008 Jul 5;376(2):416-28. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2008.03.034. Epub 2008 May 5. Virology. 2008. PMID: 18456301 Free PMC article.
-
Positive Regulation of Splicing of Cellular and Viral mRNA by Intragenic RNA Elements That Activate the Stress Kinase PKR, an Antiviral Mechanism.Genes (Basel). 2023 Apr 26;14(5):974. doi: 10.3390/genes14050974. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37239334 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Viral strategies to subvert the mammalian translation machinery.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2009;90:313-67. doi: 10.1016/S1877-1173(09)90009-6. Epub 2009 Oct 27. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2009. PMID: 20374746 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The adenovirus E1B 55-kilodalton and E4 open reading frame 6 proteins limit phosphorylation of eIF2alpha during the late phase of infection.J Virol. 2009 Oct;83(19):9970-82. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01113-09. Epub 2009 Jul 15. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19605483 Free PMC article.
-
Newcastle Disease Virus V Protein Degrades Mitochondrial Antiviral Signaling Protein To Inhibit Host Type I Interferon Production via E3 Ubiquitin Ligase RNF5.J Virol. 2019 Aug 28;93(18):e00322-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00322-19. Print 2019 Sep 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31270229 Free PMC article.
-
A single amino acid residue change in the P protein of parainfluenza virus 5 elevates viral gene expression.J Virol. 2008 Sep;82(18):9123-33. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00289-08. Epub 2008 Jul 9. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18614634 Free PMC article.
-
Measles virus circumvents the host interferon response by different actions of the C and V proteins.J Virol. 2008 Sep;82(17):8296-306. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00108-08. Epub 2008 Jun 18. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18562542 Free PMC article.
-
Zoonotic Potential of Emerging Paramyxoviruses: Knowns and Unknowns.Adv Virus Res. 2017;98:1-55. doi: 10.1016/bs.aivir.2016.12.001. Epub 2017 Feb 2. Adv Virus Res. 2017. PMID: 28433050 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Burgui, I., T. Aragon, J. Ortin, and A Nieto. 2003. PABP1 and eIF4GI associate with influenza A virus NS1 protein in viral mRNA translation initiation complexes. J. Gen. Virol. 843263-3274. - PubMed
-
- Carlos, T. S., D. Young, S. Stertz, G. Kochs, and R. E. Randall. 2007. Interferon-induced inhibition of parainfluenza virus type 5; the roles of MxA, PKR and oligo A synthetase/RNAse L. Virology 363166-173. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

