Disparity channels in early vision
- PMID: 17978018
- PMCID: PMC2376798
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4164-07.2007
Disparity channels in early vision
Erratum in
- J Neurosci. 2007 Dec 26;27(52):14525
Abstract
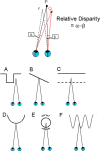
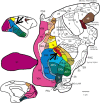
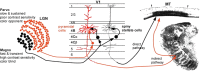
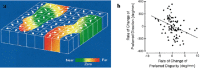
The past decade has seen a dramatic increase in our knowledge of the neural basis of stereopsis. New cortical areas have been found to represent binocular disparities, new representations of disparity information (e.g., relative disparity signals) have been uncovered, the first topographic maps of disparity have been measured, and the first causal links between neural activity and depth perception have been established. Equally exciting is the finding that training and experience affects how signals are channeled through different brain areas, a flexibility that may be crucial for learning, plasticity, and recovery of function. The collective efforts of several laboratories have established stereo vision as one of the most productive model systems for elucidating the neural basis of perception. Much remains to be learned about how the disparity signals that are initially encoded in primary visual cortex are routed to and processed by extrastriate areas to mediate the diverse capacities of three-dimensional vision that enhance our daily experience of the world.
Figures

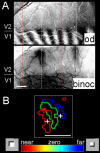
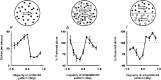
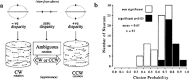
References
-
- Albright TD, Desimone R, Gross CG. Columnar organization of directionally selective cells in visual area MT of the macaque. J Neurophysiol. 1984;51:16–31. - PubMed
-
- Archie KA, Mel BW. A model for intradendritic computation of binocular disparity. Nat Neurosci. 2000;3:54–63. - PubMed
-
- Bishop PO, Pettigrew JD. Neural mechanisms of binocular vision. Vision Res. 1986;26:1587–1600. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
