Neurokinin-1 receptor enhances TRPV1 activity in primary sensory neurons via PKCepsilon: a novel pathway for heat hyperalgesia
- PMID: 17978048
- PMCID: PMC6673346
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0496-07.2007
Neurokinin-1 receptor enhances TRPV1 activity in primary sensory neurons via PKCepsilon: a novel pathway for heat hyperalgesia
Abstract
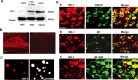
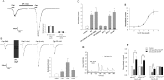
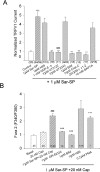
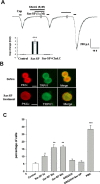
The neuropeptide substance P (SP) is expressed in unmyelinated primary sensory neurons and represents the best known "pain" neurotransmitter. It is generally believed that SP regulates pain transmission and sensitization by acting on neurokinin-1 receptor (NK-1), which is expressed in postsynaptic dorsal horn neurons. However, the expression and role of NK-1 in primary sensory neurons are not clearly characterized. Our data showed that NK-1 was expressed in both intact and dissociated dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons. In particular, NK-1 was mainly coexpressed with the capsaicin receptor TRPV1 (transient receptor potential vanilloid subtype 1), a critical receptor for the generation of heat hyperalgesia. NK-1 agonist [Sar(9), Met(O2)(11)]-substance P (Sar-SP) significantly potentiated capsaicin-induced currents and increase of [Ca2+]i in dissociated DRG neurons. NK-1 antagonist blocked not only the potentiation of TRPV1 currents but also heat hyperalgesia induced by intraplantar Sar-SP. NK-1 antagonist also inhibited capsaicin-induced spontaneous pain, and this inhibition was enhanced after inflammation. To analyze intracellular cross talking of NK-1 and TRPV1, we examined downstream signal pathways of G-protein-coupled NK-1 activation. Sar-SP-induced potentiation of TRPV1 was blocked by inhibition of G-protein, PLCbeta (phospholipase C-beta), or PKC but not by inhibition of PKA (protein kinase A). In particular, PKCepsilon inhibitor completely blocked both Sar-SP-induced TRPV1 potentiation and heat hyperalgesia. Sar-SP also induced membrane translocation of PKCepsilon in a portion of small DRG neurons. These results reveal a novel mechanism of NK-1 in primary sensory neurons via a possible autocrine and paracrine action of SP. Activation of NK-1 in these neurons induces heat hyperalgesia via PKCepsilon-mediated potentiation of TRPV1.
Figures


References
-
- Akasu T, Ishimatsu M, Yamada K. Tachykinins cause inward current through NK1 receptors in bullfrog sensory neurons. Brain Res. 1996;713:160–167. - PubMed
-
- Amadesi S, Nie JJ, Vergnolle N, Cottrell GS, Grady EF, Trevisani M, Manni C, Geppetti P, McRoberts JA, Ennes H, Davis B, Mayer EA, Bunnett NW. Protease-activated receptor 2 sensitizes the capsaicin receptor transient receptor potential vanilloid receptor 1 to induce hyperalgesia. J Neurosci. 2004;24:4300–4312. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andoh T, Nagasawa T, Kuraishi Y. Expression of tachykinin NK1 receptor mRNA in dorsal root ganglia of the mouse. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1996;35:329–332. - PubMed
-
- Bhave G, Zhu WG, Wang HB, Brasier DJ, Oxford GS, Gereau RW. cAMP-dependent protein kinase regulates desensitization of the capsaicin receptor (VR1) by direct phosphorylation. Neuron. 2002;35:721–731. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
