Cortical network dynamics during source memory retrieval: current density imaging with individual MRI
- PMID: 17979123
- PMCID: PMC6870677
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.20487
Cortical network dynamics during source memory retrieval: current density imaging with individual MRI
Abstract
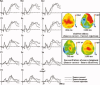
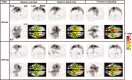
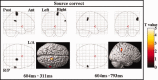
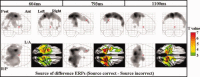
We investigated the neural correlates of source memory retrieval using low-resolution electromagnetic tomography (LORETA) with 64 channels EEG and individual MRI as a realistic head model. Event-related potentials (ERPs) were recorded while 13 healthy subjects performed the source memory task for the voice of the speaker in spoken words. The source correct condition of old words elicited more positive-going potentials than the correct rejection condition of new words at 400-700 ms post-stimulus and the old/new effects also appeared in the right anterior region between 1,000 and 1,200 ms. We conducted source reconstruction at mean latencies of 311, 604, 793, and 1,100 ms and used statistical parametric mapping for the statistical analysis. The results of source analysis suggest that the activation of the right inferior parietal region may reflect retrieval of source information. The source elicited by the difference ERPs between the source correct and source incorrect conditions exhibited dynamic change of current density activation in the overall cortices with time during source memory retrieval. These results indicate that multiple neural systems may underlie the ability to recollect context.
(c) 2007 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Alhaj HA,Massey AE,McAllister‐Williams RH ( 2005): Effects of DHEA administration on episodic memory, cortisol and mood in healthy young men: A double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study. Psychopharmacology 18: 1–11. - PubMed
-
- Allan K,Wilding EL,Rugg MD ( 1998): Electrophysiological evidence for dissociable processes contributing to recollection. Acta Psychologica 98: 231–252. - PubMed
-
- Buckner RL,Wheeler ME ( 2001): The cognitive neuroscience of remembering. Nat Rev Neurosci 2: 624–634. - PubMed
-
- Burgess PW,Shallice T ( 1996): Confabulation and the control of recollection. Memory 4: 359–411. - PubMed
-
- Burgess N,Maguire EA,Spiers HJ,O'Keefe J ( 2001): A temporoparietal and prefrontal network for retrieving the spatial context of lifelike events. Neuroimage 14: 439–453. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

