DLC-1:a Rho GTPase-activating protein and tumour suppressor
- PMID: 17979893
- PMCID: PMC4401278
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2007.00098.x
DLC-1:a Rho GTPase-activating protein and tumour suppressor
Abstract
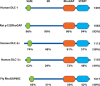
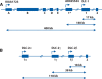
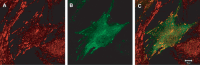
The deleted in liver cancer 1 (DLC-1) gene encodes a GTPase activating protein that acts as a negative regulator of the Rho family of small GTPases. Rho proteins transduce signals that influence cell morphology and physiology, and their aberrant up-regulation is a key factor in the neoplastic process, including metastasis. Since its discovery, compelling evidence has accumulated that demonstrates a role for DLC-1 as a bona fide tumour suppressor gene in different types of human cancer. Loss of DLC-1 expression mediated by genetic and epigenetic mechanisms has been associated with the development of many human cancers, and restoration of DLC-1 expression inhibited the growth of tumour cells in vivo and in vitro. Two closely related genes, DLC-2 and DLC-3, may also be tumour suppressors. This review presents the current status of progress in understanding the biological functions of DLC-1 and its relatives and their roles in neoplasia.
Figures


References
-
- Van Aelst L, D'Souza-Schorey C. Rho GTPases and signaling networks. Genes Dev. 1997;11:2295–322. - PubMed
-
- Ridley AJ. Rho family proteins: coordinating cell responses. Trends Cell Biol. 2001;11:471–7. - PubMed
-
- Jaffe AB, Hall A. Rho-GTPases: biochemistry and biology. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2005;21:247–69. - PubMed
-
- Sahai E, Marshall CJ. Rho-GTPases and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:133–42. - PubMed
-
- Gomez del Pulgar T, Benitah SA, Valeron PF, Espina C, Lacal JC. Rho GTPase expression in tumourigenesis: evidence for a significant link. Bioessays. 2005;27:602–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

