Generating disulfides with the Quiescin-sulfhydryl oxidases
- PMID: 17980160
- PMCID: PMC2374921
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2007.10.002
Generating disulfides with the Quiescin-sulfhydryl oxidases
Abstract
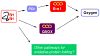
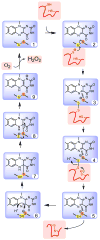
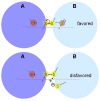
The Quiescin-sulfhydryl oxidase (QSOX) family of flavoenzymes catalyzes the direct and facile insertion of disulfide bonds into unfolded reduced proteins with concomitant reduction of oxygen to hydrogen peroxide. This review discusses the chemical mechanism of these enzymes and the involvement of thioredoxin and flavin-binding domains in catalysis. The variability of CxxC motifs in the QSOX family is highlighted and attention is drawn to the steric factors that may promote efficient thiol/disulfide exchange during oxidative protein folding. The varied cellular location of these multi-domain sulfhydryl oxidases is reviewed and potential intracellular and extracellular roles are summarized. Finally, this review identifies important unresolved questions concerning this ancient family of sulfhydryl oxidases.
Figures

References
-
- Kiermeier F, Ranfft K. About Some Characteristics of Sulfhydryloxidase in Milk. Z Lebensm-Unters-Forsch. 1970;143:11–15.
-
- Kiermeier F, Petz E. A Sulfhydryl group-oxidizing Enzyme in milk: II Influence of heating on milk and whey. Z Lebensm-Unters-Forsch. 1967;134:97–102.
-
- Swaisgood H, Janolino V. Mammalian sulfhydryl oxidase. Food Science and Technology. 2003;122:539–546.
-
- Janolino VG, Swaisgood HE. Isolation and characterization of sulfhydryl oxidase from bovine milk. J Biol Chem. 1975;250:2532–2538. - PubMed
-
- Janolino VG, Swaisgood HE. Sulfhydryl oxidase-catalyzed formation of disulfide bonds in reduced ribonuclease. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987;258:265–271. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

