Age-related changes in orolingual motor function in F344 vs F344/BN rats
- PMID: 17980393
- PMCID: PMC2350110
- DOI: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2007.10.004
Age-related changes in orolingual motor function in F344 vs F344/BN rats
Abstract
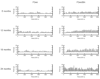
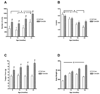
Normal aging is associated with both locomotor and orolingual motor deficits. Preclinical studies of motor function in normal aging, however, have focused primarily on locomotor activity. The purpose of this study was to measure age-related changes in orolingual motor function and compare these changes between two rat strains commonly used in aging studies: Fischer 344 (F344) and Fischer 344/Brown Norway hybrid (F344/BN) rats. Rats (6-, 12-, 18- and 24-months of age) were trained to lick water from an isometric force-sensing operandum so that the number of licks per session, licking rhythm (licks/second) and lick force could be measured. In both strains, the number of licks per session was greatest in the oldest group, while this measure was greater for F344/BN rats at all ages. Peak tongue force increased with age in F344/BN rats, did not change with age in the F344 rats, and was greater for the F344/BN rats at all ages. Both strains exhibited an age-related slowing of licking rhythm beginning with the 18-month-old group. These findings suggest that despite lifespan differences between these two rat strains, diminished tongue motility emerges at the same age.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differential effects of amphetamine and GBR-12909 on orolingual motor function in young vs aged F344/BN rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014 Dec;231(24):4695-701. doi: 10.1007/s00213-014-3620-4. Epub 2014 Jun 13. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014. PMID: 24923981 Free PMC article.
-
Aged Fischer 344 rats exhibit altered orolingual motor function: relationships with nigrostriatal neurochemical measures.Neurobiol Aging. 2003 Mar-Apr;24(2):259-66. doi: 10.1016/s0197-4580(02)00083-0. Neurobiol Aging. 2003. PMID: 12498959
-
Acute and rebound effects of lorazepam on orolingual motor function in young versus aged Fischer 344/Brown Norway rats.Behav Pharmacol. 2008 Mar;19(2):161-5. doi: 10.1097/FBP.0b013e3282f62c53. Behav Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18332681
-
Behavioral assessment of aging in male Fischer 344 and brown Norway rat strains and their F1 hybrid.Neurobiol Aging. 1994 May-Jun;15(3):319-28. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(94)90027-2. Neurobiol Aging. 1994. PMID: 7936056
-
Licking behavior in the rat: measurement and situational control of licking frequency.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1998 Oct;22(6):751-60. doi: 10.1016/s0149-7634(98)00003-7. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1998. PMID: 9809310 Review.
Cited by
-
Absence of morphological and molecular correlates of sarcopenia in the macaque tongue muscle styloglossus.Exp Gerontol. 2016 Nov;84:40-48. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2016.08.010. Epub 2016 Aug 24. Exp Gerontol. 2016. PMID: 27566374 Free PMC article.
-
Age-related increase in food spilling by laboratory mice may lead to significant overestimation of actual food consumption: implications for studies on dietary restriction, metabolism, and dose calculations.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2012 Oct;67(10):1043-8. doi: 10.1093/gerona/gls009. Epub 2012 Mar 26. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2012. PMID: 22451471 Free PMC article.
-
Age-related sex differences in tongue strength and muscle morphometry in a rat model.Arch Oral Biol. 2023 Nov;155:105779. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2023.105779. Epub 2023 Aug 1. Arch Oral Biol. 2023. PMID: 37556980 Free PMC article.
-
A high-salt diet further impairs age-associated declines in cognitive, behavioral, and cardiovascular functions in male Fischer brown Norway rats.J Nutr. 2013 Sep;143(9):1406-13. doi: 10.3945/jn.113.177980. Epub 2013 Jul 17. J Nutr. 2013. PMID: 23864508 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in growth-related kinases in head, neck and limb muscles with age.Exp Gerontol. 2011 Apr;46(4):282-91. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2010.11.004. Epub 2010 Nov 21. Exp Gerontol. 2011. PMID: 21095226 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbs JH, Hartman DE, Vishwanat B. Orofacial motor control impairment in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology. 1987;37:394–398. - PubMed
-
- Aldes LD, Champman ME, Chronister RB, Haycock JW. Sources of noradrenergic afferents to the hypoglossal nucleus in the rat. Brain Res Bull. 1992;29:931–942. - PubMed
-
- Baum BJ, Bodner L. Aging and oral motor function: evidence for altered performance among older persons. J Dent Res. 1983;62:2–6. - PubMed
-
- Behan M, Brownfield MS. Age-related changes in serotonin in the hypoglossal nucleus of the rat: implications for sleep-disordered breathing. Neurosci Lett. 1999;267:133–136. - PubMed
-
- Bennett DA, Beckett LA, Murray AM, Shannon KM, Goetz CG, Pilgrim DM, Evans DA. Prevalence of parkinsonian signs and associated mortality in a community population of older people. N Engl J Med. 1996;334:71–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

