Gout in the UK and Germany: prevalence, comorbidities and management in general practice 2000-2005
- PMID: 17981913
- PMCID: PMC2564789
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2007.076232
Gout in the UK and Germany: prevalence, comorbidities and management in general practice 2000-2005
Abstract
Objective: To investigate and compare the prevalence, comorbidities and management of gout in practice in the UK and Germany.
Methods: A retrospective analysis of patients with gout, identified through the records of 2.5 million patients in UK general practices and 2.4 million patients attending GPs or internists in Germany, using the IMS Disease Analyzer.
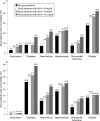
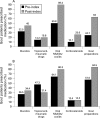
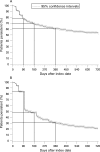
Results: The prevalence of gout was 1.4% in the UK and Germany. Obesity was the most common comorbidity in the UK (27.7%), but in Germany the most common comorbidity was diabetes (25.9%). The prevalence of comorbidities tended to increase with serum uric acid (sUA) levels. There was a positive correlation between sUA level and the frequency of gout flares. Compared with those in whom sUA was <360 micromol/l (<6 mg/dl), odds ratios for a gout flare were 1.33 and 1.37 at sUA 360-420 micromol/l (6-7 mg/dl), and 2.15 and 2.48 at sUA >530 micromol/l ( >9 mg/dl) in the UK and Germany, respectively (p<0.01).
Conclusions: The prevalence of gout in practice in the UK and Germany in the years 2000-5 was 1.4%, consistent with previous UK data for 1990-9. Chronic comorbidities were common among patients with gout and included conditions associated with an increased risk for cardiovascular disease, such as obesity, diabetes and hypertension. The importance of regular monitoring of sUA in order to tailor gout treatment was highlighted by data from this study showing that patients with sUA levels >or=360 micromol/l (>or=6 mg/dl) had an increased risk of gout flares.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Sarawate CA, Patel PA, Schumacher HR, Yang W, Brewer KK, Bakst AW. Serum urate levels and gout flares: analysis from managed care data. J Clin Rheumatol 2006;12:61–5 - PubMed
-
- Campion EW, Glynn RJ, DeLabry LO. Asymptomatic hyperuricemia. Risks and consequences in the Normative Aging Study. Am J Med 1987;82:421–6 - PubMed
-
- Becker MA, Schumacher HR, Jr, Wortmann RL, MacDonald PA, Eustace D, Palo WA, et al. Febuxostat compared with allopurinol in patients with hyperuricemia and gout. N Engl J Med 2005;353:2450–61 - PubMed
-
- Perez-Ruiz F, Calabozo M, Pijoan JI, Herrero-Beites AM, Ruibal A. Effect of urate-lowering therapy on the velocity of size reduction of tophi in chronic gout. Arthritis Rheum 2002;47:356–60 - PubMed
-
- Monu JU, Pope TL., Jr Gout: a clinical and radiologic review. Radiol Clin North Am 2004;42:169–84 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

