Sex differences in the mechanism of Met5-enkephalin-induced cardioprotection: role of PI3K/Akt
- PMID: 17982014
- PMCID: PMC2596724
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00845.2007
Sex differences in the mechanism of Met5-enkephalin-induced cardioprotection: role of PI3K/Akt
Abstract
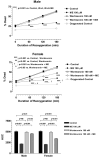
Met(5)-enkephalin (ME)-induced cardioprotection occurs via epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) transactivation with the subsequent activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K). In the present study, we investigated whether there is a sex difference in ME-elicited PI3K signaling. Neonatal murine cardiomyocytes were isolated by collagenase digestion and subjected to 90 min hypoxia and 180 min reoxygenation at 37 degrees C (n = 5 to 7 replicates). PI3K/Akt signaling was interrogated using pharmacological inhibitors and small interfering RNA (siRNA). Cell death was assessed by propidium iodide. More than 300 cells were examined for each treatment. The data are presented as means +/- SE. There was not a sex difference in the basal content of total Akt. ME (100 microM) elicited comparable protection in both sexes. Wortmannin and the nonselective Akt inhibitor IV completely abolished ME-induced protection in male cardiomyocytes but only attenuated protection in female cardiomyocytes. Isoform-selective knockdown of Akt in males with siRNAs against Akt1/2 completely abolished ME-induced cardioprotection, whereas the siRNAs against Akt3 only attenuated protection of approximately 40%. In contrast, in females the siRNAs against Akt1/2 attenuated and against Akt3 eliminated ME-induced cardioprotection. There is not a sex difference in the degree of ME-induced protection, and there is a sex difference in the cardioprotective signaling pathways after the administration of ME; ME-induced cardioprotection in males primarily utilizes a PI3K/Akt1/2 pathway and in females primarily utilizes a PI3K/Akt3 pathway. The incomplete loss of protection in females following the blockade of PI3K suggests that additional factors may facilitate the maintenance or function of activated Akt.
Figures





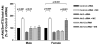
Similar articles
-
Cardioprotection induced by hydrogen sulfide preconditioning involves activation of ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways.Pflugers Arch. 2008 Jan;455(4):607-16. doi: 10.1007/s00424-007-0321-4. Epub 2007 Aug 1. Pflugers Arch. 2008. PMID: 17674030
-
Lipopolysaccharide-induced myocardial protection against ischaemia/reperfusion injury is mediated through a PI3K/Akt-dependent mechanism.Cardiovasc Res. 2008 Jun 1;78(3):546-53. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvn037. Epub 2008 Feb 11. Cardiovasc Res. 2008. PMID: 18267957
-
TLR2 ligands induce cardioprotection against ischaemia/reperfusion injury through a PI3K/Akt-dependent mechanism.Cardiovasc Res. 2010 Sep 1;87(4):694-703. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvq116. Epub 2010 Apr 26. Cardiovasc Res. 2010. PMID: 20421349 Free PMC article.
-
Met5-enkephalin-induced cardioprotection occurs via transactivation of EGFR and activation of PI3K.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005 Apr;288(4):H1955-64. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00256.2004. Epub 2004 Nov 24. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15563540
-
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibition in cancer treatment.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2001 Jun;10(6):1085-98. doi: 10.1517/13543784.10.6.1085. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2001. PMID: 11772237 Review.
Cited by
-
Sex-based differences in cardiac ischaemic injury and protection: therapeutic implications.Br J Pharmacol. 2014 Feb;171(3):541-54. doi: 10.1111/bph.12270. Br J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 23750471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gender differences and survival after an out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Intern Emerg Med. 2021 Apr;16(3):765-775. doi: 10.1007/s11739-020-02552-4. Epub 2020 Nov 10. Intern Emerg Med. 2021. PMID: 33174152
-
A new mechanism for the sex differences in angiotensin II-induced hypertension: the role of macula densa NOS1β-mediated tubuloglomerular feedback.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2020 Nov 1;319(5):F908-F919. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00312.2020. Epub 2020 Oct 12. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2020. PMID: 33044868 Free PMC article.
-
The Akt1 isoform is an essential mediator of ischaemic preconditioning.J Cell Mol Med. 2012 Aug;16(8):1739-49. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2011.01491.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22117619 Free PMC article.
-
Pathways to ischemic neuronal cell death: are sex differences relevant?J Transl Med. 2008 Jun 23;6:33. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-6-33. J Transl Med. 2008. PMID: 18573200 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abramov D, Tamariz MG, Sever JY, Christakis GT, Bhatnagar G, Heenan AL, Goldman BS, Fremes SE. The influence of gender on the outcome of coronary artery bypass surgery. Ann Thorac Surg. 2000;70:800–805. - PubMed
-
- Arensburg J, Payne AH, Orly J. Expression of steroidogenic genes in maternal and extraembryonic cells during early pregnancy in mice. Endocrinology. 1999;140:5220–5232. - PubMed
-
- Bae S, Zhang L. Gender differences in cardioprotection against ischemia/reperfusion injury in adult rat hearts: focus on Akt and protein kinase C signaling. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005;315:1125–1135. - PubMed
-
- Barrett-Conner E. Sex differences in coronary heart disease. Why are women so superior? The 1995 Ancel Keys lecture. Circulation. 1997;95:252–264. - PubMed
-
- Booth EA, Marchesi M, Kilbourne EJ, Lucchesi BR. 17beta-Estradiol as a receptor-mediated cardioprotective agent. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003;307:395–401. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

