Two independent alleles at 6q23 associated with risk of rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 17982456
- PMCID: PMC2652744
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.2007.27
Two independent alleles at 6q23 associated with risk of rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
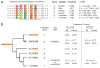
To identify susceptibility alleles associated with rheumatoid arthritis, we genotyped 397 individuals with rheumatoid arthritis for 116,204 SNPs and carried out an association analysis in comparison to publicly available genotype data for 1,211 related individuals from the Framingham Heart Study. After evaluating and adjusting for technical and population biases, we identified a SNP at 6q23 (rs10499194, approximately 150 kb from TNFAIP3 and OLIG3) that was reproducibly associated with rheumatoid arthritis both in the genome-wide association (GWA) scan and in 5,541 additional case-control samples (P = 10(-3), GWA scan; P < 10(-6), replication; P = 10(-9), combined). In a concurrent study, the Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium (WTCCC) has reported strong association of rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility to a different SNP located 3.8 kb from rs10499194 (rs6920220; P = 5 x 10(-6) in WTCCC). We show that these two SNP associations are statistically independent, are each reproducible in the comparison of our data and WTCCC data, and define risk and protective haplotypes for rheumatoid arthritis at 6q23.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests Statement: The authors declare competing financial interests: details accompany the full-text HTML version of the paper at
Figures


References
-
- Herbert A, et al. A common genetic variant is associated with adult and childhood obesity. Science. 2006;312:279–283. - PubMed
-
- Irigoyen P, et al. Regulation of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis: contrasting effects of HLA-DR3 and the shared epitope alleles. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52:3813–3818. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

