Specific developmental disruption of disrupted-in-schizophrenia-1 function results in schizophrenia-related phenotypes in mice
- PMID: 17984054
- PMCID: PMC2084334
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0706900104
Specific developmental disruption of disrupted-in-schizophrenia-1 function results in schizophrenia-related phenotypes in mice
Abstract
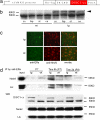
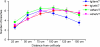
Disrupted-in-schizophrenia 1 (DISC1) was initially discovered through a balanced translocation (1;11)(q42.1;q14.3) that results in loss of the C terminus of the DISC1 protein, a region that is thought to play an important role in brain development. Here, we use an inducible and reversible transgenic system to demonstrate that early postnatal, but not adult induction, of a C-terminal portion of DISC1 in mice results in a cluster of schizophrenia-related phenotypes, including reduced hippocampal dendritic complexity, depressive-like traits, abnormal spatial working memory, and reduced sociability. Accordingly, we report that individuals in a discordant twin sample with a DISC1 haplotype, associating with schizophrenia as well as working memory impairments and reduced gray matter density, were more likely to show deficits in sociability than those without the haplotype. Our findings demonstrate that alterations in DISC1 function during brain development contribute to schizophrenia pathogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Cannon TD, Bearden CE, Hollister JM, Rosso IM, Sanchez LE, Hadley T. Schizophr Bull. 2000;26:379–393. - PubMed
-
- Selemon LD, Goldman-Rakic PS. Biol Psychiatry. 1999;45:17–25. - PubMed
-
- Lipska BK, Weinberger DR. Neurotox Res. 2002;4:469–475. - PubMed
-
- Arnold SE, Talbot K, Hahn CG. Prog Brain Res. 2005;147:319–345. - PubMed
-
- Weinberger DR. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1987;44:660–669. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

