Twenty-first century brain banking. Processing brains for research: the Columbia University methods
- PMID: 17985145
- PMCID: PMC2292479
- DOI: 10.1007/s00401-007-0311-9
Twenty-first century brain banking. Processing brains for research: the Columbia University methods
Abstract
Carefully categorized postmortem human brains are crucial for research. The lack of generally accepted methods for processing human postmortem brains for research persists. Thus, brain banking is essential; however, it cannot be achieved at the cost of the teaching mission of the academic institution by routing brains away from residency programs, particularly when the autopsy rate is steadily decreasing. A consensus must be reached whereby a brain can be utilizable for diagnosis, research, and teaching. The best diagnostic categorization possible must be secured and the yield of samples for basic investigation maximized. This report focuses on integrated, novel methods currently applied at the New York Brain Bank, Columbia University, New York, which are designed to reach accurate neuropathological diagnosis, optimize the yield of samples, and process fresh-frozen samples suitable for a wide range of modern investigations. The brains donated for research are processed as soon as possible after death. The prosector must have a good command of the neuroanatomy, neuropathology, and the protocol. One half of each brain is immersed in formalin for performing the thorough neuropathologic evaluation, which is combined with the teaching task. The contralateral half is extensively dissected at the fresh state. The anatomical origin of each sample is recorded using the map of Brodmann for the cortical samples. The samples are frozen at -160 degrees C, barcode labeled, and ready for immediate disbursement once categorized diagnostically. A rigorous organization of freezer space, coupled to an electronic tracking system with its attached software, fosters efficient access for retrieval within minutes of any specific frozen samples in storage. This report describes how this achievement is feasible with emphasis on the actual processing of brains donated for research.
Figures
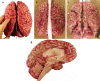
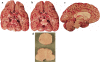
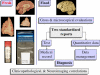
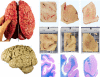

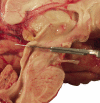



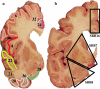




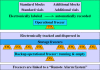
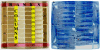


Comment in
-
Twenty-first century brain banking: at the crossroads.Acta Neuropathol. 2008 May;115(5):493-6. doi: 10.1007/s00401-008-0363-5. Acta Neuropathol. 2008. PMID: 18347804
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb04607.x', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb04607.x'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '34670', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34670/'}]}
- Albrecht J, Yanagihara T (1979) Effect of anoxia and ischemia on ribonuclease activity in brain. J Neurochem 32:1131–1133 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC6578676', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6578676/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '8774439', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8774439/'}]}
- Anderson AJ, Su JH, Cotman CW (1996) DNA damage and apoptosis in Alzheimer’s disease: colocalization with c-Jun immunoreactivity, relationship to brain area, and effect of postmortem delay. J Neurosci 16:1710–1719 - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC1083246', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC1083246/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '125784', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/125784/'}]}
- Aquilonius SM, Eckernäs SA, Sundwall A (1975) Regional distribution of choline actyltransferase in the human brain: changes in Huntington’s chorea. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 38:669–677 - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/S0891-0618(01)00099-0', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/s0891-0618(01)00099-0'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '11470556', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11470556/'}]}
- Bahn S, Augood SJ, Ryan M, Standaert DG, Starkey M, Emson PC (2001) Gene expression profiling in the post-mortem human brain––no cause for dismay. J Chem Neuroanat 22:79–94 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03532.x', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03532.x'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '7685811', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7685811/'}]}
- Barton AJ, Pearson RC, Najlerahim A, Harrison PJ (1993) Pre- and postmortem influences on brain RNA. J Neurochem 61:1–11 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

