Small-scale, semi-automated purification of eukaryotic proteins for structure determination
- PMID: 17985212
- PMCID: PMC2668602
- DOI: 10.1007/s10969-007-9032-5
Small-scale, semi-automated purification of eukaryotic proteins for structure determination
Abstract
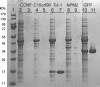
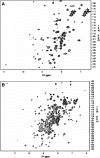
A simple approach that allows cost-effective automated purification of recombinant proteins in levels sufficient for functional characterization or structural studies is described. Studies with four human stem cell proteins, an engineered version of green fluorescent protein, and other proteins are included. The method combines an expression vector (pVP62K) that provides in vivo cleavage of an initial fusion protein, a factorial designed auto-induction medium that improves the performance of small-scale production, and rapid, automated metal affinity purification of His8-tagged proteins. For initial small-scale production screening, single colony transformants were grown overnight in 0.4 ml of auto-induction medium, produced proteins were purified using the Promega Maxwell 16, and purification results were analyzed by Caliper LC90 capillary electrophoresis. The yield of purified [U-15N]-His8-Tcl-1 was 7.5 microg/ml of culture medium, of purified [U-15N]-His8-GFP was 68 microg/ml, and of purified selenomethione-labeled AIA-GFP (His8 removed by treatment with TEV protease) was 172 microg/ml. The yield information obtained from a successful automated purification from 0.4 ml was used to inform the decision to scale-up for a second meso-scale (10-50 ml) cell growth and automated purification. 1H-15N NMR HSQC spectra of His8-Tcl-1 and of His8-GFP prepared from 50 ml cultures showed excellent chemical shift dispersion, consistent with well folded states in solution suitable for structure determination. Moreover, AIA-GFP obtained by proteolytic removal of the His8 tag was subjected to crystallization screening, and yielded crystals under several conditions. Single crystals were subsequently produced and optimized by the hanging drop method. The structure was solved by molecular replacement at a resolution of 1.7 A. This approach provides an efficient way to carry out several key target screening steps that are essential for successful operation of proteomics pipelines with eukaryotic proteins: examination of total expression, determination of proteolysis of fusion tags, quantification of the yield of purified protein, and suitability for structure determination.
Figures






Similar articles
-
High-throughput protein purification and quality assessment for crystallization.Methods. 2011 Sep;55(1):12-28. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2011.07.010. Epub 2011 Aug 31. Methods. 2011. PMID: 21907284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A rapid and universal tandem-purification strategy for recombinant proteins.Protein Sci. 2007 Dec;16(12):2726-32. doi: 10.1110/ps.072894407. Epub 2007 Oct 26. Protein Sci. 2007. PMID: 17965191 Free PMC article.
-
A simple and efficient expression and purification system using two newly constructed vectors.Protein Expr Purif. 2009 Feb;63(2):102-11. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2008.09.008. Epub 2008 Sep 20. Protein Expr Purif. 2009. PMID: 18845260 Free PMC article.
-
A family of E. coli expression vectors for laboratory scale and high throughput soluble protein production.BMC Biotechnol. 2006 Mar 1;6:12. doi: 10.1186/1472-6750-6-12. BMC Biotechnol. 2006. PMID: 16509985 Free PMC article.
-
Chapter 3. High-throughput protein purification for x-ray crystallography and NMR.Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2008;75:85-105. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3233(07)75003-9. Epub 2009 Feb 26. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2008. PMID: 20731990 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Center for Eukaryotic Structural Genomics.J Struct Funct Genomics. 2009 Apr;10(2):165-79. doi: 10.1007/s10969-008-9057-4. Epub 2009 Jan 8. J Struct Funct Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19130299 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for selective activation of ABA receptors.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2010 Sep;17(9):1109-13. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1898. Epub 2010 Aug 22. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20729860 Free PMC article.
-
Wheat germ cell-free translation, purification, and assembly of a functional human stearoyl-CoA desaturase complex.Protein Expr Purif. 2008 Dec;62(2):171-8. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2008.08.002. Epub 2008 Aug 15. Protein Expr Purif. 2008. PMID: 18765284 Free PMC article.
-
Cleavable C-terminal His-tag vectors for structure determination.J Struct Funct Genomics. 2010 Mar;11(1):31-9. doi: 10.1007/s10969-010-9082-y. Epub 2010 Mar 6. J Struct Funct Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20213425 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid, robotic, small-scale protein production for NMR screening and structure determination.Protein Sci. 2010 Mar;19(3):570-8. doi: 10.1002/pro.335. Protein Sci. 2010. PMID: 20073081 Free PMC article.
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1006/abio.2001.5331', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.2001.5331'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '11567530', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11567530/'}]}
- Knaust RK, Nordlund P (2001) Screening for soluble expression of recombinant proteins in a 96-well format. Anal Biochem 297:79–85 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/S0969-2126(00)00193-3', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/s0969-2126(00)00193-3'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '10986469', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10986469/'}]}
- Stevens RC (2000) Design of high-throughput methods of protein production for structural biology. Structure 8:R177–185 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1006/bbrc.2000.4229', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.2000.4229'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '11162598', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11162598/'}]}
- Kawasaki M, Inagaki F (2001) Random PCR-based screening for soluble domains using green fluorescent protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 280:842–844 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1074/jbc.M512588200', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m512588200'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '16717101', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16717101/'}]}
- King DA, Hall BE, Iwamoto MA, Win KZ, Chang JF, Ellenberger T (2006) Domain structure and protein interactions of the silent information regulator Sir3 revealed by screening a nested deletion library of protein fragments. J Biol Chem 281:20107–20119 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1110/ps.062082606', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1110/ps.062082606'}, {'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC2242398', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2242398/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '17008718', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17008718/'}]}
- Reich S, Puckey LH, Cheetham CL, Harris R, Ali AA, Bhattacharyya U, Maclagan K, Powell KA, Prodromou C, Pearl LH, Driscoll PC, Savva R (2006) Combinatorial domain hunting: an effective approach for the identification of soluble protein domains adaptable to high-throughput applications. Protein Sci 15:2356–2365 - PMC - PubMed

