Inhibition of vesicular monoamine transporter-2 activity in alpha-synuclein stably transfected SH-SY5Y cells
- PMID: 17985233
- PMCID: PMC11514991
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-007-9227-0
Inhibition of vesicular monoamine transporter-2 activity in alpha-synuclein stably transfected SH-SY5Y cells
Abstract
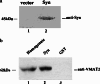
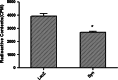
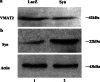
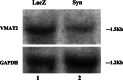
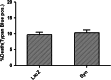
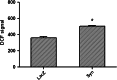
alpha-Synuclein plays a key role in the pathological neurodegeneration in Parkinson's disease. Although its contribution to normal physiology remains elusive, the selective degeneration of alpha-synuclein-containing dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson's disease may be linked to abnormal alpha-synuclein induced toxicity. In the present study, a complex of alpha-synuclein and vesicular monoamine transporter-2 was identified by GST-Pull Down experiment. In wild-type alpha-synuclein stably transfected SH-SY5Y cell lines, the activity of vesicular monoamine transporter-2 decreased by 31% as determined by [(3)H] dopamine uptake, and its expression also decreased in both protein and mRNA levels using western and northern blot analysis. Overexpression of wild-type alpha-synuclein did not induce cell death or apoptosis, but significantly enhanced the intracellular reactive oxygen species level as assayed by flow cytometry. These data suggest that Up-regulated alpha-synuclein expression inhibits the activity of vesicular monoamine transporter-2, thereby interrupting dopamine homeostasis and resulting in dopaminergic neuron injury in Parkinson's disease.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

