Subtle genetic changes enhance virulence of methicillin resistant and sensitive Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 17986343
- PMCID: PMC2222628
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2180-7-99
Subtle genetic changes enhance virulence of methicillin resistant and sensitive Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
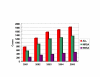
Background: Community acquired (CA) methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) increasingly causes disease worldwide. USA300 has emerged as the predominant clone causing superficial and invasive infections in children and adults in the USA. Epidemiological studies suggest that USA300 is more virulent than other CA-MRSA. The genetic determinants that render virulence and dominance to USA300 remain unclear.
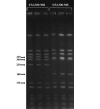
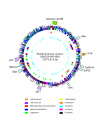
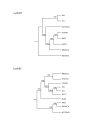
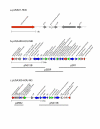
Results: We sequenced the genomes of two pediatric USA300 isolates: one CA-MRSA and one CA-methicillin susceptible (MSSA), isolated at Texas Children's Hospital in Houston. DNA sequencing was performed by Sanger dideoxy whole genome shotgun (WGS) and 454 Life Sciences pyrosequencing strategies. The sequence of the USA300 MRSA strain was rigorously annotated. In USA300-MRSA 2658 chromosomal open reading frames were predicted and 3.1 and 27 kilobase (kb) plasmids were identified. USA300-MSSA contained a 20 kb plasmid with some homology to the 27 kb plasmid found in USA300-MRSA. Two regions found in US300-MRSA were absent in USA300-MSSA. One of these carried the arginine deiminase operon that appears to have been acquired from S. epidermidis. The USA300 sequence was aligned with other sequenced S. aureus genomes and regions unique to USA300 MRSA were identified.
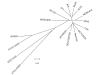
Conclusion: USA300-MRSA is highly similar to other MRSA strains based on whole genome alignments and gene content, indicating that the differences in pathogenesis are due to subtle changes rather than to large-scale acquisition of virulence factor genes. The USA300 Houston isolate differs from another sequenced USA300 strain isolate, derived from a patient in San Francisco, in plasmid content and a number of sequence polymorphisms. Such differences will provide new insights into the evolution of pathogens.
Figures

References
-
- Coombs GW, Nimmo GR, Bell JM, Huygens F, O'Brien FG, Malkowski MJ, Pearson JC, Stephens AJ, Giffard PM. Genetic diversity amongcommunity methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains causing outpatient infections in Australia. J Clin Microbiol. 2004;42:4735–4743. doi: 10.1128/JCM.42.10.4735-4743.2004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen CJ, Huang YC. Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Taiwan. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2005;38:376–382. - PubMed
-
- Hanssen AM, Fossum A, Mikalsen J, Halvorsen DS, Bukholm G, Sollid JU. Dissemination of community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clones in northern Norway: sequence types 8 and 80 predominate. J Clin Microbiol. 2005;43:2118–2124. doi: 10.1128/JCM.43.5.2118-2124.2005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

